Involvement of hypoxia-inducible transcription factors in polycystic kidney disease
- PMID: 17322369
- PMCID: PMC1864863
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060455
Involvement of hypoxia-inducible transcription factors in polycystic kidney disease
Abstract
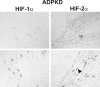
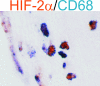
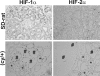
In polycystic kidney disease (PKD), erythropoietin (EPO) production and interstitial vascularization are increased compared with other kidney diseases. EPO and several angiogenic factors are controlled by hypoxia-inducible transcription factors (HIFs), which are composed of a constitutive beta-subunit and two alternative alpha-subunits (HIF-1alpha, HIF-2alpha). We hypothesized that cyst expansion may result in pericystic hypoxia and consecutive up-regulation of HIF and thus examined the expression of HIF-alpha and HIF target genes in human PKD and in a rodent PKD model. HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha were found to be up-regulated in cyst epithelium and cells of cyst walls, respectively. The distinct expression pattern of the HIF-alpha isoforms closely resembles the respective pattern in normal kidneys under systemic hypoxia. Pimonidazole staining, a marker for tissue hypoxia, confirmed the existence of regional hypoxia in polycystic kidneys. Immunohistochemistry for selected target genes implicated a role for HIF-1alpha in vascular endothelial growth factor and Glut-1 activation and HIF-2alpha in endoglin and EPO stimulation. Polycystin-deficient cells showed physiological, oxygen-dependent HIF-alpha modulation, excluding a direct influence of polycystin deficiency on HIF-alpha regulation. In conclusion, HIF accumulation in human and rat PKD seems to be responsible for increased EPO production and pericystic hypervascularity and may have an impact on progression of PKD.
Figures



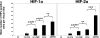
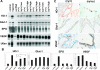

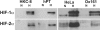
References
-
- Wilson PD. Polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:151–164. - PubMed
-
- Gabow PA. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:332–342. - PubMed
-
- Cowley BD., Jr Recent advances in understanding the pathogenesis of polycystic kidney disease: therapeutic implications. Drugs. 2004;64:1285–1294. - PubMed
-
- Maïz HB, Abderrahim E, Zouaghi K. Anemia and end-stage renal disease in the developing world. Artif Organs. 2002;26:760–764. - PubMed
-
- Abbott KC, Agodoa LY. Polycystic kidney disease at end-stage renal disease in the United States: patient characteristics and survival. Clin Nephrol. 2002;57:208–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

