Dickkopf-1 regulates gastrulation movements by coordinated modulation of Wnt/beta catenin and Wnt/PCP activities, through interaction with the Dally-like homolog Knypek
- PMID: 17322405
- PMCID: PMC1804334
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.406007
Dickkopf-1 regulates gastrulation movements by coordinated modulation of Wnt/beta catenin and Wnt/PCP activities, through interaction with the Dally-like homolog Knypek
Abstract
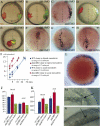
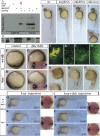
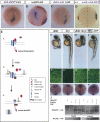
Dickkopf-1 (Dkk1) is a secreted protein that negatively modulates the Wnt/beta catenin pathway. Lack of Dkk1 function affects head formation in frog and mice, supporting the idea that Dkk1 acts as a "head inducer" during gastrulation. We show here that lack of Dkk1 function accelerates internalization and rostral progression of the mesendoderm and that gain of function slows down both internalization and convergence extension, indicating a novel role for Dkk1 in modulating these movements. The motility phenotype found in the morphants is not observed in embryos in which the Wnt/beta catenin pathway is overactivated, and that dominant-negative Wnt proteins are not able to rescue the gastrulation movement defect induced by absence of Dkk1. These data strongly suggest that Dkk1 is acting in a beta catenin independent fashion when modulating gastrulation movements. We demonstrate that the glypican 4/6 homolog Knypek (Kny) binds to Dkk1 and that they are able to functionally interact in vivo. Moreover, Dkk1 regulation of gastrulation movements is kny dependent. Kny is a component of the Wnt/planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway. We found that indeed Dkk1 is able to activate this pathway in both Xenopus and zebrafish. Furthermore, concomitant alteration of the beta catenin and PCP activities is able to mimic the morphant accelerated cell motility phenotype. Our data therefore indicate that Dkk1 regulates gastrulation movement through interaction with LRP5/6 and Kny and coordinated modulations of Wnt/beta catenin and Wnt/PCP pathways.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Role of glypican 4 in the regulation of convergent extension movements during gastrulation in Xenopus laevis.Development. 2003 May;130(10):2129-38. doi: 10.1242/dev.00435. Development. 2003. PMID: 12668627
-
Molecular analysis of a self-organizing signaling pathway for Xenopus axial patterning from egg to tailbud.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jul 9;121(28):e2408346121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2408346121. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38968117 Free PMC article.
-
Waif1/5T4 inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling and activates noncanonical Wnt pathways by modifying LRP6 subcellular localization.Dev Cell. 2011 Dec 13;21(6):1129-43. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.10.015. Epub 2011 Nov 17. Dev Cell. 2011. PMID: 22100263
-
Non-canonical Wnt signalling and regulation of gastrulation movements.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2002 Jun;13(3):251-60. doi: 10.1016/s1084-9521(02)00052-6. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2002. PMID: 12137734 Review.
-
Heads or tails? Amphioxus and the evolution of anterior-posterior patterning in deuterostomes.Dev Biol. 2002 Jan 15;241(2):209-28. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2001.0503. Dev Biol. 2002. PMID: 11784106 Review.
Cited by
-
Lrp6 is required for convergent extension during Xenopus gastrulation.Development. 2007 Nov;134(22):4095-106. doi: 10.1242/dev.010272. Development. 2007. PMID: 17965054 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish Naked1 and Naked2 antagonize both canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling.Dev Biol. 2007 Sep 15;309(2):151-68. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.04.018. Epub 2007 Apr 21. Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17689523 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic interaction between Lrp6 and Wnt5a during mouse development.Dev Dyn. 2010 Jan;239(1):237-45. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22101. Dev Dyn. 2010. PMID: 19795512 Free PMC article.
-
High throughput identification of monoclonal antibodies to membrane bound and secreted proteins using yeast and phage display.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 29;9(10):e111339. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111339. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25353955 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt3 and Wnt3a are required for induction of the mid-diencephalic organizer in the caudal forebrain.Neural Dev. 2012 Apr 4;7:12. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-7-12. Neural Dev. 2012. PMID: 22475147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn S., Joyner A.L., Joyner A.L. Dynamic changes in the response of cells to positive hedgehog signaling during mouse limb patterning. Cell. 2004;118:505–516. - PubMed
-
- Axelrod J.D., Miller J.R., Shulman J.M., Moon R.T., Perrimon N., Miller J.R., Shulman J.M., Moon R.T., Perrimon N., Shulman J.M., Moon R.T., Perrimon N., Moon R.T., Perrimon N., Perrimon N. Differential recruitment of Dishevelled provides signaling specificity in the planar cell polarity and Wingless signaling pathways. Genes & Dev. 1998;12:2610–2622. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belenkaya T.Y., Han C., Yan D., Opoka R.J., Khodoun M., Liu H., Lin X., Han C., Yan D., Opoka R.J., Khodoun M., Liu H., Lin X., Yan D., Opoka R.J., Khodoun M., Liu H., Lin X., Opoka R.J., Khodoun M., Liu H., Lin X., Khodoun M., Liu H., Lin X., Liu H., Lin X., Lin X. Drosophila Dpp morphogen movement is independent of dynamin-mediated endocytosis but regulated by the glypican members of heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Cell. 2004;119:231–244. - PubMed
-
- Boutros M., Paricio N., Strutt D.I., Mlodzik M., Paricio N., Strutt D.I., Mlodzik M., Strutt D.I., Mlodzik M., Mlodzik M. Dishevelled activates JNK and discriminates between JNK pathways in planar polarity and wingless signaling. Cell. 1998;94:109–118. - PubMed
-
- Brembeck F.H., Rosario M., Birchmeier W., Rosario M., Birchmeier W., Birchmeier W. Balancing cell adhesion and Wnt signaling, the key role of β-catenin. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2006;16:51–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
