Development of a monoclonal antibody-based co-agglutination test to detect enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from diarrheic neonatal calves
- PMID: 17322775
- PMCID: PMC2872698
- DOI: 10.4142/jvs.2007.8.1.57
Development of a monoclonal antibody-based co-agglutination test to detect enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from diarrheic neonatal calves
Abstract
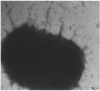
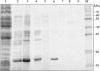
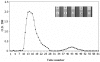
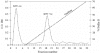
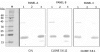
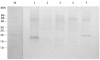
Escherichia coli (E. coli) strains were collected from young diarrheic calves in farms and field. Strains that expressed the K99 (F5) antigen were identified by agglutination tests using reference antibodies to K99 antigen and electron microscopy. The K99 antigen from a selected field strain (SAR-14) was heat-extracted and fractionated on a Sepharose CL-4B column. Further purification was carried out by sodium deoxycholate treatment and/or ion-exchange chromatography. Monoclonal antibodies to purified K99 antigen were produced by the hybridoma technique, and a specific clone, NEK99-5.6.12, was selected for propagation in tissue culture. The antibodies, thus obtained, were affinity-purified, characterized and coated onto Giemsastained Cowan-I strain of Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus). The antibody-coated S. aureus were used in a coagglutination test to detect K99+ E. coli isolated from feces of diarrheic calves. The specificity of the test was validated against reference monoclonal antibodies used in co-agglutination tests, as well as in ELISA. Specificity of the monoclonal antibodies was also tested against various Gram negative bacteria. The developed antibodies specifically detected purified K99 antigen in immunoblots, as well as K99+ E. coli in ELISA and co-agglutination tests. The co-agglutination test was specific and convenient for large-scale screening of K99+ E. coli isolates.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, using monoclonal antibody, to detect enterotoxic Escherichia coli K99 antigen in feces of dairy calves.Am J Vet Res. 1984 Dec;45(12):2613-6. Am J Vet Res. 1984. PMID: 6395737
-
Evaluation of a monoclonal antibody to the K99 fimbrial adhesin produced by Escherichia coli enterotoxigenic for calves, lambs and piglets.Res Vet Sci. 1985 Jul;39(1):75-9. Res Vet Sci. 1985. PMID: 2412267
-
Isolation by phage display of recombinant antibodies able to block adherence of Escherichia coli mediated by the K99 colonisation factor.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2008 Feb 15;121(3-4):321-31. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2007.10.005. Epub 2007 Oct 12. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2008. PMID: 18036670
-
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infections in newborn calves: a review.J Dairy Sci. 1985 Jan;68(1):229-56. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(85)80814-6. J Dairy Sci. 1985. PMID: 2579990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bovine enteric colibacillosis.Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 1985 Nov;1(3):495-508. doi: 10.1016/s0749-0720(15)31298-6. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 1985. PMID: 3907783 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular screening and risk factors of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. in diarrheic neonatal calves in Egypt.Res Vet Sci. 2009 Dec;87(3):373-9. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2009.04.006. Epub 2009 May 5. Res Vet Sci. 2009. PMID: 19419742 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Batra HV, Chand P, Thillaikoothan P, Talwar GP. Coagglutination test with coloured Staphylococcus aureus for detection of brucella antigens in cattle brucellosis. Vet Rec. 1987;121:65–66. - PubMed
-
- Boedeker EC. Vaccines for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: current status. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2005;21:15–19. - PubMed
-
- Chakraborty S, Deokule JS, Garg P, Bhattacharya SK, Nandy RK, Nair GB, Yamasaki S, Takeda Y, Ramamurthy T. Concomitant infection of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in an outbreak of cholera caused by Vibrio cholerae O1 and O139 in Ahmedabad, India. J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39:3241–3246. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

