Population-based resequencing of ANGPTL4 uncovers variations that reduce triglycerides and increase HDL
- PMID: 17322881
- PMCID: PMC2762948
- DOI: 10.1038/ng1984
Population-based resequencing of ANGPTL4 uncovers variations that reduce triglycerides and increase HDL
Abstract
Resequencing genes provides the opportunity to assess the full spectrum of variants that influence complex traits. Here we report the first application of resequencing to a large population (n = 3,551) to examine the role of the adipokine ANGPTL4 in lipid metabolism. Nonsynonymous variants in ANGPTL4 were more prevalent in individuals with triglyceride levels in the lowest quartile than in individuals with levels in the highest quartile (P = 0.016). One variant (E40K), present in approximately 3% of European Americans, was associated with significantly lower plasma levels of triglyceride and higher levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in European Americans from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study and in Danes from the Copenhagen City Heart Study. The ratio of nonsynonymous to synonymous variants was higher in European Americans than in African Americans (4:1 versus 1.3:1), suggesting population-specific relaxation of purifying selection. Thus, resequencing of ANGPTL4 in a multiethnic population allowed analysis of the phenotypic effects of both rare and common variants while taking advantage of genetic variation arising from ethnic differences in population history.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures

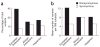
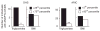
Comment in
-
The resequencing imperative.Nat Genet. 2007 Apr;39(4):439-40. doi: 10.1038/ng0407-439. Nat Genet. 2007. PMID: 17392801 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rondinone CM. Adipocyte-derived hormones, cytokines, and mediators. Endocrine. 2006;29:81–90. - PubMed
-
- Li C. Genetics and regulation of angiopoietin-like proteins 3 and 4. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2006;17:152–156. - PubMed
-
- Koster A, et al. Transgenic angiopoietin-like (angptl)4 overexpression and targeted disruption of angptl4 and angptl3: regulation of triglyceride metabolism. Endocrinology. 2005;146:4943–4950. - PubMed
-
- Yoshida K, Shimizugawa T, Ono M, Furukawa H. Angiopoietin-like protein 4 is a potent hyperlipidemia-inducing factor in mice and inhibitor of lipoprotein lipase. J Lipid Res. 2002;43:1770–1772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

