HLA-DRB1*0404 is strongly associated with anticalpastatin antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 17324966
- PMCID: PMC2095311
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2006.067231
HLA-DRB1*0404 is strongly associated with anticalpastatin antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
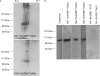
Objective: To test whether HLA-DR alleles influence the production of particular autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, we screened synovial proteins with sera of RA patients homozygous for different HLA-DR alleles by using 2D blots. We found that sera of RA patients homozygous for HLA-DRB1*0404 recognised a 100-kDa synovial protein identified as calpastatin. We studied B and T cell epitopes on calpastatin and their association with HLA-DRB1*0404.
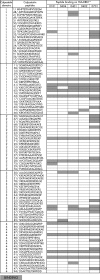
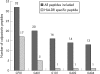
Methods: The frequency of positive sera in patients expressing different RA-associated HLA-DR allele combinations was calculated by inhouse ELISA using purified synovial calpastatin or calpastatin peptides encompassing the entire calpastatin protein as immunosorbent. Interaction between calpastatin peptides and HLA-DR alleles was tested by a direct binding assay. T cell responses to calpastatin were measured in RA patients and controls.
Results: We found that RA-associated HLA-DR alleles are associated with presence of autoantibodies to synovial calpastatin in RA patients' sera. HLA-DRB1*0404 is strongly associated with antisynovial calpastatin in RA sera. One linear B cell epitope is preferentially associated with HLA-DRB1*0404. Multiple peptides from calpastatin bind every tested HLA-DR allele associated or not with RA. Peptides from domain 1 and 4 of calpastatin are the best HLA-DR allele binders. The T cell response to calpastatin is frequent in RA patients and independent of the HLA-DR background.
Conclusions: HLA-DRB1*0404 is strongly associated with anticalpastatin antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Similar articles
-
Influence of HLA-DR genes on the production of rheumatoid arthritis-specific autoantibodies to citrullinated fibrinogen.Arthritis Rheum. 2005 Nov;52(11):3424-32. doi: 10.1002/art.21391. Arthritis Rheum. 2005. PMID: 16255019
-
Interferon-gamma production in response to in vitro stimulation with collagen type II in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with HLA-DRB1(*)0401 and HLA-DQ8.Arthritis Res. 2000;2(1):75-84. doi: 10.1186/ar71. Arthritis Res. 2000. PMID: 11219392 Free PMC article.
-
Association between HLA class II genes and autoantibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptides (CCPs) influences the severity of rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Jul;50(7):2113-21. doi: 10.1002/art.20316. Arthritis Rheum. 2004. PMID: 15248208
-
How RA Associated HLA-DR Molecules Contribute to the Development of Antibodies to Citrullinated Proteins: The Hapten Carrier Model.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 10;13:930112. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.930112. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35774784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
To B or not to B: role of B cells in pathogenesis of arthritis in HLA transgenic mice.J Autoimmun. 2011 Sep;37(2):95-103. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2011.05.002. Epub 2011 Jun 12. J Autoimmun. 2011. PMID: 21665435 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-citrullinated peptide antibody-negative RA is a genetically distinct subset: a definitive study using only bone-erosive ACPA-negative rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010 Dec;49(12):2298-304. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keq273. Epub 2010 Sep 9. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010. PMID: 20833643 Free PMC article.
-
HLA-DRB1 allele distribution and its relation to rheumatoid arthritis in eastern Black Sea Turkish population.Rheumatol Int. 2012 Apr;32(4):1003-7. doi: 10.1007/s00296-010-1792-8. Epub 2011 Jan 19. Rheumatol Int. 2012. PMID: 21246357
-
T cells in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S1. doi: 10.1186/ar2412. Epub 2008 Oct 15. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008. PMID: 19007421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autoantibodies to BRAF, a new family of autoantibodies associated with rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(5):R194. doi: 10.1186/ar3165. Epub 2010 Oct 18. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20955560 Free PMC article.
-
PAD2 immunization induces ACPA in wild-type and HLA-DR4 humanized mice.Eur J Immunol. 2022 Sep;52(9):1464-1473. doi: 10.1002/eji.202249889. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Eur J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35712879 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Symmons D P M. What is rheumatoid arthritis? Br Med Bull 199551243–248. - PubMed
-
- Gregersen P K, Silver J, Winchester R J. The shared epitope hypothesis: an approach to understanding the molecular genetics of susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1987301205–1213. - PubMed
-
- Menard H A, El‐Amine M. The calpain–calpastatin system in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Today 199617545–547. - PubMed
-
- Lackner K J, Schlosser U, Lang B, Schmitz G. Autoantibodies against human calpastatin in rheumatoid arthritis: epitope mapping and analysis of patient sera. Br J Rheumatol 1998371164–1171. - PubMed
-
- Vittecoq O, Salle V, Jouen‐Beades F, Krzanowska K, Menard J F, Gayet A.et al Autoantibodies to the 27 C‐terminal amino acids of calpastatin are detected in a restricted set of connective tissue diseases and may be useful for diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis in community cases of very early arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001401126–1134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials