Very low blood hydroxychloroquine concentration as an objective marker of poor adherence to treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 17324970
- PMCID: PMC1954674
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2006.067835
Very low blood hydroxychloroquine concentration as an objective marker of poor adherence to treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Background: Poor adherence to treatment is difficult to diagnose accurately. Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) has a long elimination half-life and its concentration in whole blood can be measured easily.
Objective: To evaluate the utility of a very low blood HCQ concentration as a marker of poor compliance in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Methods: HCQ concentrations were determined on a blinded basis in 203 unselected patients with SLE. At the end of the study, the patients were informed of the results and retrospectively interviewed about their adherence to treatment.
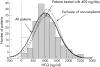
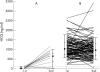
Results: 14 (7%) patients said that they had stopped taking HCQ (n = 8) or had taken it no more than once or twice a week (n = 6). Their mean (SD) HCQ concentration was 26 (46) ng/ml. range (0-129 ng/ml) By contrast, the other patients had a mean HCQ concentration of 1079 ng/ml range (205-2629 ng/ml). The principal barriers to adherence were related to HCQ treatment characteristics. Adherence subsequently improved in 10 of the 12 patients whose blood HCQ concentrations were remeasured.
Conclusions: Very low whole-blood HCQ concentrations are an objective marker of prolonged poor compliance in patients with SLE. Regular drug assays might help doctors in detect non-compliance and serve as a basis for counselling and supporting these patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None.
References
-
- Osterberg L, Blaschke T. Drug therapy: adherence to medication. N Engl J Med 2005353487–497. - PubMed
-
- Petri M, Perez‐Gutthann S, Longenecker J C, Hochberg M. Morbidity of systemic lupus erythematosus: role of race and socioeconomic status. Am J Med 199191345–353. - PubMed
-
- Mosley‐Williams A, Lumley M A, Gillis M, Leisen J, Guice D. Barriers to treatment adherence among African American and white women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 200247630–638. - PubMed
-
- Mirotznik J, Ginzler E, Zagon G, Baptiste A. Using the health belief model to explain clinic appointment‐keeping for the management of a chronic disease condition. J Community Health 199823195–210. - PubMed