Alpha E beta 7 integrin interaction with E-cadherin promotes antitumor CTL activity by triggering lytic granule polarization and exocytosis
- PMID: 17325197
- PMCID: PMC2137907
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20061524
Alpha E beta 7 integrin interaction with E-cadherin promotes antitumor CTL activity by triggering lytic granule polarization and exocytosis
Abstract
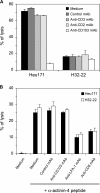
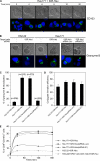
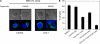
Various T cell adhesion molecules and their cognate receptors on target cells promote T cell receptor (TCR)-mediated cell killing. In this report, we demonstrate that the interaction of epithelial cell marker E-cadherin with integrin alpha(E)(CD103)beta(7), often expressed by tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), plays a major role in effective tumor cell lysis. Indeed, we found that although tumor-specific CD103(+) TIL-derived cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) clones are able to kill E-cadherin(+)/intercellular adhesion molecule 1(-) autologous tumor cells, CD103(-) peripheral blood lymphocyte (PBL)-derived counterparts are inefficient. This cell killing is abrogated after treatment of the TIL clones with a blocking anti-CD103 monoclonal antibody or after targeting E-cadherin in the tumor using ribonucleic acid interference. Confocal microscopy analysis also demonstrated that alpha(E)beta(7) is recruited at the immunological synapse and that its interaction with E-cadherin is required for cytolytic granule polarization and subsequent exocytosis. Moreover, we report that the CD103(-) profile, frequently observed in PBL-derived CTL clones and associated with poor cytotoxicity against the cognate tumor, is up-regulated upon TCR engagement and transforming growth factor beta1 treatment, resulting in strong potentiation of antitumor lytic function. Thus, CD8(+)/CD103(+) tumor-reactive T lymphocytes infiltrating epithelial tumors most likely play a major role in antitumor cytotoxic response through alpha(E)beta(7)-E-cadherin interactions.
Figures



References
-
- Bossi, G., C. Trambas, S. Booth, R. Clark, J. Stinchcombe, and G.M. Griffiths. 2002. The secretory synapse: the secrets of a serial killer. Immunol. Rev. 189:152–160. - PubMed
-
- Monks, C.R., B.A. Freiberg, H. Kupfer, N. Sciaky, and A. Kupfer. 1998. Three-dimensional segregation of supramolecular activation clusters in T cells. Nature. 395:82–86. - PubMed
-
- Huppa, J.B., and M.M. Davis. 2003. T-cell-antigen recognition and the immunological synapse. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3:973–983. - PubMed
-
- Stinchcombe, J.C., G. Bossi, S. Booth, and G.M. Griffiths. 2001. The immunological synapse of CTL contains a secretory domain and membrane bridges. Immunity. 15:751–761. - PubMed
-
- Kuhn, J.R., and M. Poenie. 2002. Dynamic polarization of the microtubule cytoskeleton during CTL-mediated killing. Immunity. 16:111–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

