Focal adhesion kinase modulates tension signaling to control actin and focal adhesion dynamics
- PMID: 17325207
- PMCID: PMC2064024
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200608010
Focal adhesion kinase modulates tension signaling to control actin and focal adhesion dynamics
Abstract
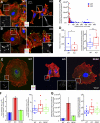
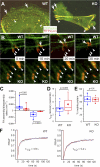
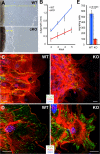
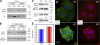
In response to alphabeta1 integrin signaling, transducers such as focal adhesion kinase (FAK) become activated, relaying to specific machineries and triggering distinct cellular responses. By conditionally ablating Fak in skin epidermis and culturing Fak-null keratinocytes, we show that FAK is dispensable for epidermal adhesion and basement membrane assembly, both of which require alphabeta1 integrins. FAK is also dispensible for proliferation/survival in enriched medium. In contrast, FAK functions downstream of alphabeta1 integrin in regulating cytoskeletal dynamics and orchestrating polarized keratinocyte migration out of epidermal explants. Fak-null keratinocytes display an aberrant actin cytoskeleton, which is tightly associated with robust, peripheral focal adhesions and microtubules. We find that without FAK, Src, p190RhoGAP, and PKL-PIX-PAK, localization and/or activation at focal adhesions are impaired, leading to elevated Rho activity, phosphorylation of myosin light chain kinase, and enhanced tensile stress fibers. We show that, together, these FAK-dependent activities are critical to control the turnover of focal adhesions, which is perturbed in the absence of FAK.
Figures
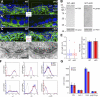
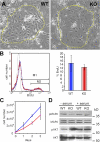
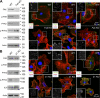
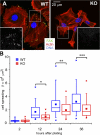
References
-
- Arthur, W.T., L.A. Petch, and K. Burridge. 2000. Integrin engagement suppresses RhoA activity via a c-Src-dependent mechanism. Curr. Biol. 10:719–722. - PubMed
-
- Astier, A., H. Avraham, S.N. Manie, J. Groopman, T. Canty, S. Avraham, and A.S. Freedman. 1997. The related adhesion focal tyrosine kinase is tyrosine-phosphorylated after beta1-integrin stimulation in B cells and binds to p130cas. J. Biol. Chem. 272:228–232. - PubMed
-
- Avizienyte, E., A.W. Wyke, R.J. Jones, G.W. McLean, M.A. Westhoff, V.G. Brunton, and M.C. Frame. 2002. Src-induced de-regulation of E-cadherin in colon cancer cells requires integrin signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 4:632–638. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

