Paradoxical elevation of high-molecular weight adiponectin in acquired extreme insulin resistance due to insulin receptor antibodies
- PMID: 17325257
- PMCID: PMC2253187
- DOI: 10.2337/db06-1665
Paradoxical elevation of high-molecular weight adiponectin in acquired extreme insulin resistance due to insulin receptor antibodies
Abstract
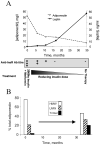
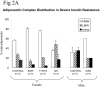
Total plasma adiponectin and high-molecular weight (HMW) polymeric adiponectin are strongly positively correlated with insulin sensitivity. However, we have recently reported paradoxical hyperadiponectinemia in patients with severe insulin resistance due to genetically defective insulin receptors. This implies either that the insulin receptor has a critical physiological role in controlling adiponectin production and/or clearance or that constitutive insulin receptor dysfunction influences adiponectin levels through developmental effects. The aim of the current study was to distinguish between these possibilities using a human model of reversible antibody-mediated insulin receptor dysfunction and to refine the previous observations by determining adiponectin complex distribution. Cross-sectional and longitudinal determination of fasting plasma adiponectin and adiponectin complex distribution was undertaken in patients with extreme insulin resistance due to insulin receptor mutations, anti-insulin receptor antibodies (type B insulin resistance), or an undefined cause. Despite extreme insulin resistance, patients with type B insulin resistance (all women; mean age 42 years [range 12-54]) had dramatically elevated total plasma adiponectin compared with the general population (mean 43.0 mg/l [range 31.3-54.2] vs. 8.9 mg/l [1.5-28.5 for BMI <25 kg/m(2)]), which was accounted for largely by HMW polymers. Hyperadiponectinemia resolved in parallel with reduction of insulin receptor antibodies and clinical resolution of insulin resistance. Although the well-established inverse relationship between plasma insulin and adiponectin levels may, in part, reflect positive effects of adiponectin on insulin sensitivity, these data suggest that the magnitude of the effect of insulin action on adiponectin levels may have been underestimated.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Elevated plasma adiponectin in humans with genetically defective insulin receptors.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Aug;91(8):3219-23. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-0166. Epub 2006 May 16. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006. PMID: 16705075
-
Altered distribution of adiponectin isoforms in children with Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS): association with insulin sensitivity and circulating satiety peptide hormones.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2007 Dec;67(6):944-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2007.02991.x. Epub 2007 Jul 30. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2007. PMID: 17666087 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma adiponectin and insulin sensitivity in overweight and normal-weight middle-aged premenopausal women.Metabolism. 2009 May;58(5):638-43. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2008.12.009. Metabolism. 2009. PMID: 19375586
-
Adiponectin Resistance in Obesity: Adiponectin Leptin/Insulin Interaction.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1460:431-462. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-63657-8_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39287861 Review.
-
Adiponectin and leptin in human severe insulin resistance - diagnostic utility and biological insights.Biochimie. 2012 Oct;94(10):2172-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2012.01.021. Epub 2012 Feb 4. Biochimie. 2012. PMID: 22342226 Review.
Cited by
-
Serum level of adiponectin correlated with gender and genotype in patients with chronic hepatitis C.Dig Dis Sci. 2009 May;54(5):1120-7. doi: 10.1007/s10620-008-0455-z. Epub 2008 Sep 5. Dig Dis Sci. 2009. PMID: 18773295
-
Chronic liquid nutrition intake induces obesity and considerable but reversible metabolic alterations in Wistar rats.J Physiol Biochem. 2016 Jun;72(2):225-43. doi: 10.1007/s13105-016-0472-x. Epub 2016 Mar 3. J Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26939586
-
Adiponectin signaling and function in insulin target tissues.J Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Apr;8(2):101-9. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjw014. Epub 2016 Mar 18. J Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26993044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Approach to Diagnosing a Pediatric Patient With Severe Insulin Resistance in Low- or Middle-income Countries.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Nov 19;106(12):3621-3633. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgab549. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34318892 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin resistance uncoupled from dyslipidemia due to C-terminal PIK3R1 mutations.JCI Insight. 2016 Oct 20;1(17):e88766. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.88766. JCI Insight. 2016. PMID: 27766312 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scherer PE. Adipose tissue: from lipid storage compartment to endocrine organ. Diabetes. 2006;55:1537–1545. - PubMed
-
- Lindsay RS, Funahashi T, Hanson RL, Matsuzawa Y, Tanaka S, Tataranni PA, Knowler WC, Krakoff J. Adiponectin and development of type 2 diabetes in the Pima Indian population. Lancet. 2002;360:57–58. - PubMed
-
- Yu JG, Javorschi S, Hevener AL, Kruszynska YT, Norman RA, Sinha M, Olefsky JM. The effect of thiazolidinediones on plasma adiponectin levels in normal, obese, and type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 2002;51:2968–2974. - PubMed
-
- Berg AH, Combs TP, Du X, Brownlee M, Scherer PE. The adipocyte-secreted protein Acrp30 enhances hepatic insulin action. Nat Med. 2001;7:947–953. - PubMed
-
- Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Waki H, Terauchi Y, Kubota N, Hara K, Mori Y, Ide T, Murakami K, Tsuboyama-Kasaoka N, Ezaki O, Akanuma Y, Gavrilova O, Vinson C, Reitman ML, Kagechika H, Shudo K, Yoda M, Nakano Y, Tobe K, Nagai R, Kimura S, Tomita M, Froguel P, Kadowaki T. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat Med. 2001;7:941–946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

