SPARC inhibits LPA-mediated mesothelial-ovarian cancer cell crosstalk
- PMID: 17325741
- PMCID: PMC1803033
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.06658
SPARC inhibits LPA-mediated mesothelial-ovarian cancer cell crosstalk
Abstract
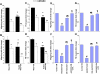
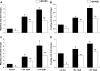
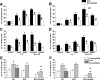
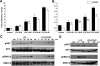
The interplay between peritoneal mesothelial cells and ovarian cancer cells is critical for the initiation and peritoneal dissemination of, and ascites formation in, ovarian cancer. The production of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) by both peritoneal mesothelial cells and ovarian cancer cells has been shown to promote metastatic phenotype in ovarian cancer. Herein, we report that exogenous addition or ectopic overexpression of the matricellular protein SPARC (secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine) significantly attenuated LPA-induced proliferation, chemotaxis, and invasion in both highly metastatic SKOV3 and less metastatic OVCAR3 ovarian cancer cell lines. SPARC appears to modulate these functions, at least in part, through the regulation of LPA receptor levels and the attenuation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 and protein kinase B/AKT signaling. Moreover, our results show that SPARC not only significantly inhibited both basal and LPA-induced interleukin (IL) 6 production in both cell lines but also attenuated IL-6-induced mitogenic, chemotactic, and proinvasive effects, in part, through significant suppression of ERK1/2 and, to a lesser extent, of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 signaling pathways. Our results strongly suggest that SPARC exerts a dual inhibitory effect on LPA-induced mesothelial-ovarian cancer cell crosstalk through the regulation of both LPA-induced IL-6 production and function. Taken together, our findings underscore the use of SPARC as a potential therapeutic candidate in peritoneal ovarian carcinomatosis.
Figures
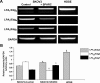
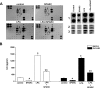

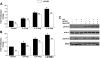
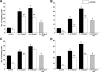
References
-
- Schwartz B, Hong G, Morrison B, Wu W, Baudhuin L, Xiao Y, Mok S, Xu Y. Lysophospholipids increase interleukin-8 expression in ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 2001;81:291–300. - PubMed
-
- Guo R, Kasbohm E, Arora P, Sample C, Baban B, Sud N, Sivashanmugam P, Moniri N, Daaka Y. Expression and function of lysophosphatidic acid LPA1 receptor in prostate cancer cells. Endocrinology. 2006;147:4883–4892. - PubMed
-
- Bian D, Su S, Mahanivong C, Cheng R, Han Q, Pan Z, Sun Pand Huang S. Lysophosphatidic acid stimulates ovarian cancer cell migration via a Ras-MEK kinase 1 pathway. Cancer Res. 2004;64:4209–4217. - PubMed
-
- Li H, Ye X, Mahanivong C, Bian D, Chun J, Huang S. Signaling mechanisms responsible for lysophosphatidic acid-induced urokinase plasminogen activator expression in ovarian cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:10564–10571. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
