Imaging techniques for small animal models of pulmonary disease: MR microscopy
- PMID: 17325972
- PMCID: PMC2747380
- DOI: 10.1080/01926230601132048
Imaging techniques for small animal models of pulmonary disease: MR microscopy
Abstract
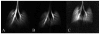
In vivo magnetic resonance microscopy (MRM) of the small animal lung has become a valuable research tool, especially for preclinical studies. MRM offers a noninvasive and nondestructive tool for imaging small animals longitudinally and at high spatial resolution. We summarize some of the technical and biologic problems and solutions associated with imaging the small animal lung and describe several important pulmonary disease applications. A major advantage of MR is direct imaging of the gas spaces of the lung using breathable gases such as helium and xenon. When polarized, these gases become rich MR signal sources. In animals breathing hyperpolarized helium, the dynamics of gas distribution can be followed and airway constrictions and obstructions can be detected. Diffusion coefficients of helium can be calculated from diffusion-sensitive images, which can reveal micro-structural changes in the lungs associated with pathologies such as emphysema and fibrosis. Unlike helium, xenon in the lung is absorbed by blood and exhibits different frequencies in gas, tissue, or erythrocytes. Thus, with MR imaging, the movement of xenon gas can be tracked through pulmonary compartments to detect defects of gas transfer. MRM has become a valuable tool for studying morphologic and functional changes in small animal models of lung diseases.
Figures

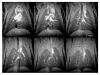
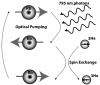
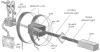
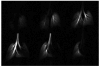
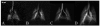


Similar articles
-
Hyperpolarized noble gas MR imaging of the lung: potential clinical applications.Eur J Radiol. 2001 Oct;40(1):33-44. doi: 10.1016/s0720-048x(01)00347-3. Eur J Radiol. 2001. PMID: 11673006
-
Hyperpolarized Gas MR Imaging: Technique and Applications.Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2015 May;23(2):217-29. doi: 10.1016/j.mric.2015.01.003. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2015. PMID: 25952516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperpolarized gas MR Imaging of the lung: current status as a research tool.J Thorac Imaging. 2009 Aug;24(3):181-8. doi: 10.1097/RTI.0b013e3181b32bec. J Thorac Imaging. 2009. PMID: 19704321 Review.
-
Functional MR imaging of pulmonary ventilation using hyperpolarized noble gases.Acta Radiol. 2000 Nov;41(6):519-28. doi: 10.1080/028418500127346009. Acta Radiol. 2000. PMID: 11092469 Review.
-
Development of hyperpolarized noble gas MRI.Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res A. 1998;402:441-53. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9002(97)00888-7. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res A. 1998. PMID: 11543065
Cited by
-
Longitudinal assessment of lung cancer progression in the mouse using in vivo micro-CT imaging.Med Phys. 2010 Sep;37(9):4793-805. doi: 10.1118/1.3476454. Med Phys. 2010. PMID: 20964199 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives of hyperpolarized noble gas MRI beyond 3He.J Magn Reson. 2013 Apr;229:173-86. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2012.11.014. Epub 2012 Dec 8. J Magn Reson. 2013. PMID: 23290627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of undersampling on preclinical lung T2* mapping with 3D radial UTE MRI at 7 T.J Magn Reson. 2024 Aug;365:107741. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2024.107741. Epub 2024 Jul 26. J Magn Reson. 2024. PMID: 39089222 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular MRI for sensitive and specific detection of lung metastases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 23;107(8):3693-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1000386107. Epub 2010 Feb 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20142483 Free PMC article.
-
Primed infusion with delayed equilibrium of Gd.DTPA for enhanced imaging of small pulmonary metastases.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54903. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054903. Epub 2013 Jan 31. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23382996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albert MS, Cates GD, Driehuys B, Happer W, Saam B, Springer CS, Wishnia A. Biological magnetic-resonance imaging using laser polarized 129Xe. Nature. 1994;370:199–201. - PubMed
-
- Albert MS, Schepkin VD, Budinger TF. Measurement of 129Xe T1 in blood to explore the feasibility of hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1995;19:975–8. - PubMed
-
- Beckmann N, Tigani B, Mazzoni L, Fozard JR. MRI of lung parenchyma in rats and mice using a gradient-echo sequence. NMR Biomed. 2001;14:297–306. - PubMed
-
- Beckmann N, Tigani B, Mazzoni L, Fozard JR. Techniques: Magnetic resonance imaging of the lung provides potential for noninvasive preclinical evaluation of drugs. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003;24:550–4. - PubMed
-
- Black RD, Middleton HL, Cates GD, Cofer GP, Driehuys B, Happer W, Hedlund LW, Johnson GA, Shattuck MD, Swartz JC. In vivo He-3 MR images of guinea pig lungs. Radiology. 1996;199:867–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

