Extracellular localization of galectin-3 has a deleterious role in joint tissues
- PMID: 17326835
- PMCID: PMC1860078
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2130
Extracellular localization of galectin-3 has a deleterious role in joint tissues
Abstract
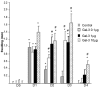
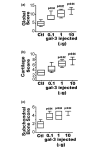
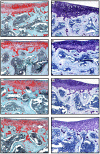
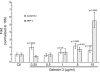
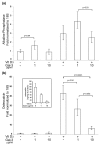
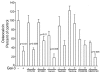
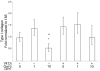
In this study we examine the extracellular role of galectin-3 (gal-3) in joint tissues. Following intra-articular injection of gal-3 or vehicle in knee joints of mice, histological evaluation of articular cartilage and subchondral bone was performed. Further studies were then performed using human osteoarthritic (OA) chondrocytes and subchondral bone osteoblasts, in which the effect of gal-3 (0 to 10 microg/ml) was analyzed. Osteoblasts were incubated in the presence of vitamin D3 (50 nM), which is an inducer of osteocalcin, encoded by an osteoblast terminal differentiation gene. Genes of interest mainly expressed in either chondrocytes or osteoblasts were analyzed with real-time RT-PCR and enzyme immunoassays. Signalling pathways regulating osteocalcin were analyzed in the presence of gal-3. Intra-articular injection of gal-3 induced knee swelling and lesions in both cartilage and subchondral bone. On human OA chondrocytes, gal-3 at 1 microg/ml stimulated ADAMTS-5 expression in chondrocytes and, at higher concentrations (5 and 10 microg/ml), matrix metalloproteinase-3 expression. Experiments performed with osteoblasts showed a weak but bipolar effect on alkaline phosphatase expression: stimulation at 1 microg/ml or inhibition at 10 microg/ml. In the absence of vitamin D3, type I collagen alpha 1 chain expression was inhibited by 10 microg/ml of gal-3. The vitamin D3 induced osteocalcin was strongly inhibited in a dose-dependent manner in the presence of gal-3, at both the mRNA and protein levels. This inhibition was mainly mediated by phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase. These findings indicate that high levels of extracellular gal-3, which could be encountered locally during the inflammatory process, have deleterious effects in both cartilage and subchondral bone tissues.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Avocado/soybean unsaponifiables prevent the inhibitory effect of osteoarthritic subchondral osteoblasts on aggrecan and type II collagen synthesis by chondrocytes.J Rheumatol. 2006 Aug;33(8):1668-78. J Rheumatol. 2006. PMID: 16832844
-
Osteoarthritic cartilage chondrocytes alter subchondral bone osteoblast differentiation via MAPK signalling pathway involving ERK1/2.Bone. 2010 Jan;46(1):226-35. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2009.10.014. Epub 2009 Oct 22. Bone. 2010. PMID: 19853676
-
The melanocortin system in articular chondrocytes: melanocortin receptors, pro-opiomelanocortin, precursor proteases, and a regulatory effect of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone on proinflammatory cytokines and extracellular matrix components.Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Oct;60(10):3017-27. doi: 10.1002/art.24846. Arthritis Rheum. 2009. PMID: 19790046
-
Cartilage degeneration in different human joints.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005 Feb;13(2):93-103. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2004.11.006. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005. PMID: 15694570 Review.
-
Osteoblast-chondrocyte interactions in osteoarthritis.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2014 Mar;12(1):127-34. doi: 10.1007/s11914-014-0192-5. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2014. PMID: 24458429 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Galectin-3 interacts with PD-1 and counteracts the PD-1 pathway-driven regulation of T cell and osteoclast activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Scand J Immunol. 2023 Feb;97(2):e13245. doi: 10.1111/sji.13245. Epub 2022 Dec 30. Scand J Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36537046 Free PMC article.
-
The Dysregulated Galectin Network Activates NF-κB to Induce Disease Markers and Matrix Degeneration in 3D Pellet Cultures of Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes.Calcif Tissue Int. 2021 Mar;108(3):377-390. doi: 10.1007/s00223-020-00774-4. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Calcif Tissue Int. 2021. PMID: 33185768 Free PMC article.
-
Human osteoarthritic knee cartilage: fingerprinting of adhesion/growth-regulatory galectins in vitro and in situ indicates differential upregulation in severe degeneration.Histochem Cell Biol. 2014 Oct;142(4):373-88. doi: 10.1007/s00418-014-1234-x. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Histochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24981556
-
Galectin network in osteoarthritis: galectin-4 programs a pathogenic signature of gene and effector expression in human chondrocytes in vitro.Histochem Cell Biol. 2022 Feb;157(2):139-151. doi: 10.1007/s00418-021-02053-1. Epub 2021 Nov 30. Histochem Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 34846578 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin 3 Deficiency Alters Chondrocyte Primary Cilium Formation and Exacerbates Cartilage Destruction via Mitochondrial Apoptosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 22;21(4):1486. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041486. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32098291 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burr DB. The importance of subchondral bone in the progression of osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol Suppl. 2004;70:77–80. - PubMed
-
- Oehler S, Neureiter D, Meyer-Scholten C, Aigner T. Subtyping of osteoarthritic synoviopathy. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2002;20:633–640. - PubMed
-
- DeGroot J, Verzijl N, Wenting-van Wijk MJ, Jacobs KM, Van El B, Van Roermund PM, Bank RA, Bijlsma JW, TeKoppele JM, Lafeber FP. Accumulation of advanced glycation end products as a molecular mechanism for aging as a risk factor in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:1207–1215. doi: 10.1002/art.20170. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

