Endothelial cell protein C receptor acts as a cellular receptor for factor VIIa on endothelium
- PMID: 17327234
- PMCID: PMC2591933
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M609283200
Endothelial cell protein C receptor acts as a cellular receptor for factor VIIa on endothelium
Abstract
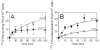
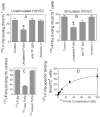
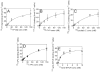
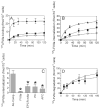
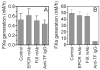
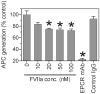
Although factor VII/factor VIIa (FVII/FVIIa) is known to interact with many non-vascular cells, activated monocytes, and endothelial cells via its binding to tissue factor (TF), the interaction of FVII/FVIIa with unperturbed endothelium and the role of this interaction in clearing FVII/FVIIa from the circulation are unknown. To investigate this, in the present study we examined the binding of radiolabeled FVIIa to endothelial cells and its subsequent internalization. (125)I-FVIIa bound to non-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) in time- and dose-dependent manner. The binding is specific and independent of TF and negatively charged phospholipids. Protein C and monoclonal antibodies to endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR) blocked effectively (125)I-FVIIa binding to HUVEC. FVIIa binding to EPCR is confirmed by demonstrating a marked increase in (125)I-FVIIa binding to CHO cells that had been stably transfected with EPCR compared with the wild-type. Binding analysis revealed that FVII, FVIIa, protein C, and activated protein C (APC) bound to EPCR with similar affinity. FVIIa binding to EPCR failed to accelerate FVIIa activation of factor X or protease-activated receptors. FVIIa binding to EPCR was shown to facilitate FVIIa endocytosis. Pharmacological concentrations of FVIIa were found to impair partly the EPCR-dependent protein C activation and APC-mediated cell signaling. Overall, the present data provide convincing evidence that EPCR serves as a cellular binding site for FVII/FVIIa. Further studies are needed to evaluate the pathophysiological consequences and relevance of FVIIa binding to EPCR.
Figures



References
-
- Fair DS. Blood. 1983;62:784–791. - PubMed
-
- Loeliger EA, van der Esch B, ter Haar Romney-Wachter CC, Booij HL. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1960;4:196–200. - PubMed
-
- Seligsohn U, Kasper CK, Osterud B, Rapaport SI. Blood. 1979;53:828–837. - PubMed
-
- Erhardtsen E. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2000;26:385–391. - PubMed
-
- Hasselback R, Hjort PF. J Appl Physiol. 1960;15:945–948. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

