Fatal hemorrhage in mice lacking gamma-glutamyl carboxylase
- PMID: 17327402
- PMCID: PMC1890832
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-12-064188
Fatal hemorrhage in mice lacking gamma-glutamyl carboxylase
Abstract
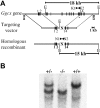
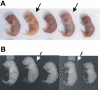
The carboxylation of glutamic acid residues to gamma-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) by the vitamin K-dependent gamma-glutamyl carboxylase (gamma-carboxylase) is an essential posttranslational modification required for the biological activity of a number of proteins, including proteins involved in blood coagulation and its regulation. Heterozygous mice carrying a null mutation at the gamma-carboxylase (Ggcx) gene exhibit normal development and survival with no evidence of hemorrhage and normal functional activity of the vitamin K-dependent clotting factors IX, X, and prothrombin. Analysis of a Ggcx(+/-) intercross revealed a partial developmental block with only 50% of expected Ggcx(-/-) offspring surviving to term, with the latter animals dying uniformly at birth of massive intra-abdominal hemorrhage. This phenotype closely resembles the partial midembryonic loss and postnatal hemorrhage previously reported for both prothrombin- and factor V (F5)-deficient mice. These data exclude the existence of a redundant carboxylase pathway and suggest that functionally critical substrates for gamma-carboxylation, at least in the developing embryo and neonate, are primarily restricted to components of the blood coagulation cascade.
Figures

References
-
- Furie B, Bouchard BA, Furie BC. Vitamin K-dependent biosynthesis of γ-carboxyglutamic acid. Blood. 1999;93:1798–1808. - PubMed
-
- Stafford DW. The vitamin K cycle. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3:1873–1878. - PubMed
-
- Romero EE, Velazquez-Estades LJ, Deo R, Schapiro B, Roth DA. Cloning of rat vitamin K-dependent γ-glutamyl carboxylase and developmentally regulated gene expression in post-implantation embryos. Exp Cell Res. 1998;243:334–346. - PubMed
-
- Hanumanthaiah R, Thankavel B, Day K, Gregory M, Jagadeeswaran P. Developmental expression of vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase activity in zebrafish embryos: effect of warfarin. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2001;27:992–999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

