Identification of uPAR-positive chemoresistant cells in small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 17327908
- PMCID: PMC1800348
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000243
Identification of uPAR-positive chemoresistant cells in small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: The urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) and its receptor (uPAR/CD87) are major regulators of extracellular matrix degradation and are involved in cell migration and invasion under physiological and pathological conditions. The uPA/uPAR system has been of great interest in cancer research because it is involved in the development of most invasive cancer phenotypes and is a strong predictor of poor patient survival. However, little is known about the role of uPA/uPAR in small cell lung cancer (SCLC), the most aggressive type of lung cancer. We therefore determined whether uPA and uPAR are involved in generation of drug resistant SCLC cell phenotype.
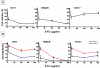
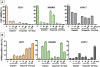
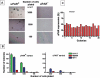
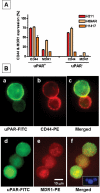
Methods and findings: We screened six human SCLC cell lines for surface markers for putative stem and cancer cells. We used fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS), fluorescence microscopy and clonogenic assays to demonstrate uPAR expression in a subpopulation of cells derived from primary and metastatic SCLC cell lines. Cytotoxic assays were used to determine the sensitivity of uPAR-positive and uPAR-negative cells to chemotherapeutic agents. The uPAR-positive cells in all SCLC lines demonstrated multi-drug resistance, high clonogenic activity and co-expression of CD44 and MDR1, putative cancer stem cell markers.
Conclusions: These data suggest that uPAR-positive cells may define a functionally important population of cancer cells in SCLC, which are resistant to traditional chemotherapies, and could serve as critical targets for more effective therapeutic interventions in SCLC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Urokinase plasminogen activator and urokinase plasminogen activator receptor mediate human stem cell tropism to malignant solid tumors.Stem Cells. 2008 Jun;26(6):1406-13. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2008-0141. Epub 2008 Apr 10. Stem Cells. 2008. PMID: 18403751
-
Interleukin-1alpha enhances the aggressive behavior of pancreatic cancer cells by regulating the alpha6beta1-integrin and urokinase plasminogen activator receptor expression.BMC Cell Biol. 2006 Feb 20;7:8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-7-8. BMC Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16504015 Free PMC article.
-
The urokinase-system in tumor tissue stroma of the breast and breast cancer cell invasion.Int J Oncol. 2009 Jan;34(1):15-23. Int J Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19082473
-
Evolving role of uPA/uPAR system in human cancers.Cancer Treat Rev. 2008 Apr;34(2):122-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2007.10.005. Epub 2007 Dec 26. Cancer Treat Rev. 2008. PMID: 18162327 Review.
-
Structure, function and expression on blood and bone marrow cells of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor, uPAR.Stem Cells. 1997;15(6):398-408. doi: 10.1002/stem.150398. Stem Cells. 1997. PMID: 9402652 Review.
Cited by
-
Strategies to Target Chemoradiotherapy Resistance in Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Oct 10;16(20):3438. doi: 10.3390/cancers16203438. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor (uPAR) in Inflammation and Disease: A Unique Inflammatory Pathway Activator.Biomedicines. 2024 May 24;12(6):1167. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061167. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Fibrinolytic System in Health and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 9;23(9):5262. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095262. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563651 Free PMC article.
-
The role of cancer stem cells in neoplasia of the lung: past, present and future.Clin Transl Oncol. 2008 Nov;10(11):719-25. doi: 10.1007/s12094-008-0278-6. Clin Transl Oncol. 2008. PMID: 19015068 Review.
-
Non-small cell lung cancer cells expressing CD44 are enriched for stem cell-like properties.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 19;5(11):e14062. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014062. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21124918 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pisick E, Jagadeesh S, Salgia R. Small cell lung cancer: from molecular biology to novel therapeutics. J Exp Ther Oncol. 2003;3:305–318. - PubMed
-
- Aguirre Ghiso JA, Alonso DF, Farias EF, Gomez DE, de Kier Joffe EB. Deregulation of the signaling pathways controlling urokinase production. Its relationship with the invasive phenotype. Eur J Biochem. 1999;263:295–304. - PubMed
-
- Aref S, El-Sherbiny M, Mabed M, Menessy A, El-Refaei M. Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor and soluble matrix metalloproteinase-9 in acute myeloid leukemia patients: a possible relation to disease invasion. Hematology. 2003;8:385–391. - PubMed
-
- Foekens JA, Peters HA, Look MP, Portengen H, Schmitt M, et al. The urokinase system of plasminogen activation and prognosis in 2780 breast cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2000;60:636–643. - PubMed
-
- Meijer-van Gelder ME, Look MP, Peters HA, Schmitt M, Brunner N, et al. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator system in breast cancer: association with tamoxifen therapy in recurrent disease. Cancer Res. 2004;64:4563–4568. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

