The role of T helper 17 (Th17) and regulatory T cells (Treg) in human organ transplantation and autoimmune disease
- PMID: 17328715
- PMCID: PMC1868863
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03356.x
The role of T helper 17 (Th17) and regulatory T cells (Treg) in human organ transplantation and autoimmune disease
Abstract
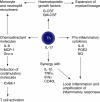
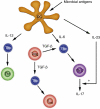
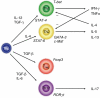
Uncommitted (naive) murine CD4+ T helper cells (Thp) can be induced to differentiate towards T helper 1 (Th1), Th2, Th17 and regulatory (Treg) phenotypes according to the local cytokine milieu. This can be demonstrated most readily both in vitro and in vivo in murine CD4+ T cells. The presence of interleukin (IL)-12 [signalling through signal transduction and activator of transcription (STAT)-4] skews towards Th1, IL-4 (signalling through STAT-6) towards Th2, transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta towards Treg and IL-6 and TGF-beta towards Th17. The committed cells are characterized by expression of specific transcription factors, T-bet for Th1, GATA-3 for Th2, forkhead box P3 (FoxP3) for Tregs and RORgammat for Th17 cells. Recently, it has been demonstrated that the skewing of murine Thp towards Th17 and Treg is mutually exclusive. Although human Thp can also be skewed towards Th1 and Th2 phenotypes there is as yet no direct evidence for the existence of discrete Th17 cells in humans nor of mutually antagonistic development of Th17 cells and Tregs. There is considerable evidence, however, both in humans and in mice for the importance of interferon (IFN)-gamma and IL-17 in the development and progression of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases (AD). Unexpectedly, some models of autoimmunity thought traditionally to be solely Th1-dependent have been demonstrated subsequently to have a non-redundant requirement for Th17 cells, notably experimental allergic encephalomyelitis and collagen-induced arthritis. In contrast, Tregs have anti-inflammatory properties and can cause quiescence of autoimmune diseases and prolongation of transplant function. As a result, it can be proposed that skewing of responses towards Th17 or Th1 and away from Treg may be responsible for the development and/or progression of AD or acute transplant rejection in humans. Blocking critical cytokines in vivo, notably IL-6, may result in a shift from a Th17 towards a regulatory phenotype and induce quiescence of AD or prevent transplant rejection. In this paper we review Th17/IL-17 and Treg biology and expand on this hypothesis.
Figures
References
-
- Starr TK, Jameson SC, Hogquist KA. Positive and negative selection of T cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:139–76. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Markovic-Plese S, Lacet B, Raus J, Weiner HL, Hafler DA. Increased frequency of interleukin 2-responsive T cells specific for myelin basic protein and proteolipid protein in peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med. 1994;179:973–84. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Markovic-Plese S, Fukaura H, Zhang J, et al. T cell recognition of immunodominant and cryptic proteolipid protein epitopes in humans. J Immunol. 1995;155:982–92. - PubMed
-
- Constant SL, Bottomly K. Induction of Th1 and Th2 CD4+ T cell responses: the alternative approaches. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:297–322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

