Expression of Toll-like receptor 9 in nose, peripheral blood and bone marrow during symptomatic allergic rhinitis
- PMID: 17328813
- PMCID: PMC1810251
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-8-17
Expression of Toll-like receptor 9 in nose, peripheral blood and bone marrow during symptomatic allergic rhinitis
Abstract
Background: Allergic rhinitis is an inflammatory disease of the upper airway mucosa that also affects leukocytes in bone marrow and peripheral blood. Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) is a receptor for unmethylated CpG dinucleotides found in bacterial and viral DNA. The present study was designed to examine the expression of TLR9 in the nasal mucosa and in leukocytes derived from different cellular compartments during symptomatic allergic rhinitis.
Methods: The study was based on 32 patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis and 18 healthy subjects, serving as controls. Nasal biopsies were obtained before and after allergen challenge. Bone marrow, peripheral blood and nasal lavage fluid were sampled outside and during pollen season. The expression of TLR9 in tissues and cells was analyzed using immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry, respectively.
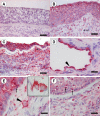
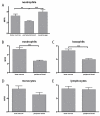
Results: TLR9 was found in several cell types in the nasal mucosa and in different leukocyte subpopulations derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood and nasal lavage fluid. The leukocyte expression was generally higher in bone marrow than in peripheral blood, and not affected by symptomatic allergic rhinitis.
Conclusion: The widespread expression of TLR9 in the nasal mucosa along with its rich representation in leukocytes in different compartments, demonstrate the possibility for cells involved in allergic airway inflammation to directly interact with bacterial and viral DNA.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nasal CpG oligodeoxynucleotide administration induces a local inflammatory response in nonallergic individuals.Allergy. 2009 Sep;64(9):1292-300. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2009.02012.x. Epub 2009 Feb 19. Allergy. 2009. PMID: 19243360 Clinical Trial.
-
Up-regulation of Toll-like receptors 2, 3 and 4 in allergic rhinitis.Respir Res. 2005 Sep 7;6(1):100. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-6-100. Respir Res. 2005. PMID: 16146574 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Systemic up-regulation of TLR4 causes lipopolysaccharide-induced augmentation of nasal cytokine release in allergic rhinitis.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2012;159(1):6-14. doi: 10.1159/000335196. Epub 2012 Apr 27. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22555057
-
Objective monitoring of nasal airway inflammation in rhinitis.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005 Mar;115(3 Suppl 1):S414-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2004.12.1134. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15746881 Review.
-
Nasal nitric oxide and nasal allergy.Allergy. 2006 Jun;61(6):665-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2006.01096.x. Allergy. 2006. PMID: 16677234 Review.
Cited by
-
A possible role for neutrophils in allergic rhinitis revealed after cellular subclassification.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 8;7:43568. doi: 10.1038/srep43568. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28272395 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory Syncytial Virus Elicits Glycolytic Metabolism in Pediatric Upper and Lower Airways.Viruses. 2025 May 14;17(5):703. doi: 10.3390/v17050703. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40431714 Free PMC article.
-
The expression and function of Nod-like receptors in neutrophils.Immunology. 2010 May;130(1):55-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03212.x. Epub 2009 Dec 2. Immunology. 2010. PMID: 20002790 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle conjugation enhances the immunomodulatory effects of intranasally delivered CpG in house dust mite-allergic mice.Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 21;5:14274. doi: 10.1038/srep14274. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26387548 Free PMC article.
-
Is The Allergen Really Needed in Allergy Immunotherapy?Curr Treat Options Allergy. 2015;2(1):72-82. doi: 10.1007/s40521-014-0038-5. Curr Treat Options Allergy. 2015. PMID: 25722959 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

