Induction of apoptosis by tumor suppressor FHIT via death receptor signaling pathway in human lung cancer cells
- PMID: 17328863
- PMCID: PMC1934611
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.02.067
Induction of apoptosis by tumor suppressor FHIT via death receptor signaling pathway in human lung cancer cells
Abstract
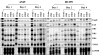
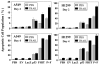
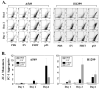
FHIT is a novel tumor suppressor gene located at human chromosome 3p14.2. Restoration of wild-type FHIT in 3p14.2-deficient human lung cancer cells inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis. In this study, we analyzed potential upstream/downstream molecular targets of the FHIT protein and found that FHIT specifically targeted and regulated death receptor (DR) genes in human non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells. Exogenous expression of FHIT by a recombinant adenoviral vector (Ad)-mediated gene transfer upregulated expression of DR genes. Treatment with a recombinant TRAIL protein, a DR-specific ligand, in Ad-FHIT-transduced NSCLC cells considerably enhanced FHIT-induced apoptosis, further demonstrating the involvement of DRs in FHIT-induced apoptosis. Moreover, we also found that FHIT targeted downstream of the DR-mediated signaling pathway. FHIT overexpression disrupted mitochondrial membrane integrity and activated multiple pro-apoptotic proteins in NSCLC cell. These results suggest that FHIT induces apoptosis through a sequential activation of DR-mediated pro-apoptotic signaling pathways in human NSCLC cells.
Figures

References
-
- Peto R, Lopez AD, Boreham J, Thun M, Heath C, Jr, Doll R. Mortality from smoking worldwide. Br Med Bull. 1996;52:12–21. - PubMed
-
- Zabarovsky ER, Lerman MI, Minna JD. Tumor suppressor genes on chromosome 3p involved in the pathogenesis of lung and other cancers. Oncogene. 2002;21:6915–6935. - PubMed
-
- Sozzi G, Pastorino U, Moiraghi L, Tagliabue E, Pezzella F, Ghirelli C, Tornielli S, Sard L, Huebner K, Pierotti MA, Croce CM, Pilotti S. Loss of FHIT function in lung cancer and preinvasive bronchial lesions. Adv Cancer Res. 1998;74:141–166. - PubMed
-
- Ji L, Fang B, Yen N, Fong K, Minna JD, Roth JA. Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of tumorigenicity and tumor growth by adenovirus vector-mediated fragile histidine triad (FHIT) gene overexpression. Cancer Res. 1999;59:3333–3339. - PubMed
-
- Pekarsky Y, Palamarchuk A, Huebner K, Croce CM. FHIT as tumor suppressor: mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Cancer Biol Ther. 2002;1:232–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

