The distributed auditory cortex
- PMID: 17329049
- PMCID: PMC2637155
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heares.2007.01.017
The distributed auditory cortex
Abstract
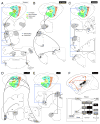
A synthesis of cat auditory cortex (AC) organization is presented in which the extrinsic and intrinsic connections interact to derive a unified profile of the auditory stream and use it to direct and modify cortical and subcortical information flow. Thus, the thalamocortical input provides essential sensory information about peripheral stimulus events, which AC redirects locally for feature extraction, and then conveys to parallel auditory, multisensory, premotor, limbic, and cognitive centers for further analysis. The corticofugal output influences areas as remote as the pons and the cochlear nucleus, structures whose effects upon AC are entirely indirect, and it has diverse roles in the transmission of information through the medial geniculate body and inferior colliculus. The distributed AC is thus construed as a functional network in which the auditory percept is assembled for subsequent redistribution in sensory, premotor, and cognitive streams contingent on the derived interpretation of the acoustic events. The confluence of auditory and multisensory streams likely precedes cognitive processing of sound. The distributed AC constitutes the largest and arguably the most complete representation of the auditory world. Many facets of this scheme may apply in rodent and primate AC as well. We propose that the distributed auditory cortex contributes to local processing regimes in regions as disparate as the frontal pole and the cochlear nucleus to construct the acoustic percept.
Figures


References
-
- Aitkin LM. Medial geniculate body of the cat: responses to tonal stimuli of neurons in medial division. J Neurophysiol. 1973;36:275–283. - PubMed
-
- Aitkin LM, Dunlop CW. Interplay of excitation and inhibition in the cat medial geniculate body. J Neurophysiol. 1968;31:44–61. - PubMed
-
- Bajo VM, Rouiller EM, Welker E, Clarke S, Villa AEP, de Ribaupierre Y, de Ribaupierre F. Morphology and spatial distribution of corticothalamic terminals originating from the cat auditory cortex. Hearing Res. 1995;83:161–174. - PubMed
-
- Bao S, Chan VT, Merzenich MM. Cortical remodelling induced by activity of ventral tegmental dopamine neurons. Nature. 2001;412:79–83. - PubMed
-
- Beneyto M, Prieto JJ. Connections of the auditory cortex with the claustrum and endopiriform nucleus in the cat. Brain Res Bull. 2001;54:485–498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

