Developmental synaptic plasticity at the thalamocortical input to barrel cortex: mechanisms and roles
- PMID: 17329121
- PMCID: PMC1952688
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcn.2007.01.001
Developmental synaptic plasticity at the thalamocortical input to barrel cortex: mechanisms and roles
Abstract
The thalamocortical (TC) input to layer IV provides the major pathway for ascending sensory information to the mammalian sensory cortex. During development there is a dramatic refinement of this input that underlies the maturation of the topographical map in layer IV. Over the last 10 years our understanding of the mechanisms of the developmental and experience-driven changes in synaptic function at TC synapses has been greatly advanced. Here we describe these studies that point to a key role for NMDA receptor-dependent synaptic plasticity, a role for kainate receptors and for a rapid maturation in GABAergic inhibition. The expression mechanisms of some of the forms of neonatal synaptic plasticity are novel and, in combination with other mechanisms, produce a layer IV circuit that exhibits functional properties necessary for mature sensory processing.
Figures

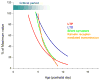
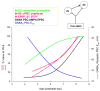
References
-
- Abdel-Majid RM, Leong WL, Schalkwyk LC, Smallman DS, Wong ST, Storm DR, Fine A, Dobson MJ, Guernsey DL, Neumann PE. Loss of adenylyl cyclase I activity disrupts patterning of mouse somatosensory cortex. Nat Genet. 1998;19:289–291. - PubMed
-
- Agmon A, Connors BW. Thalamocortical responses of mouse somatosensory (barrel) cortex in vitro. Neuroscience. 1991;41:365–379. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong-James M, Callahan CA. Thalamo-cortical processing of vibrissal information in the rat. II. spatiotemporal convergence in the thalamic ventroposterior medial nucleus (VPm) and its relevance to generation of receptive fields of S1 cortical "barrel" neurones. J Comp Neurol. 1991;303:211–224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

