Lytic and latent antigens of the human gammaherpesviruses Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus and Epstein-Barr virus induce T-cell responses with similar functional properties and memory phenotypes
- PMID: 17329344
- PMCID: PMC1900166
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02509-06
Lytic and latent antigens of the human gammaherpesviruses Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus and Epstein-Barr virus induce T-cell responses with similar functional properties and memory phenotypes
Abstract
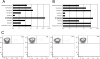
The cellular immunity against Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is poorly characterized and has not been compared to T-cell responses against other human herpesviruses. Here, novel and dominant targets of KSHV-specific cellular immunity are identified and compared to T cells specific for lytic and latent antigens in a second human gammaherpesvirus, Epstein-Barr virus. The data identify a novel HLA-B57- and HLA-B58-restricted epitope in the Orf57 protein and show consistently close parallels in immune phenotypes and functional response patterns between cells targeting lytic or latent KSHV- and EBV-encoded antigens, suggesting common mechanisms in the induction of these responses.
Figures

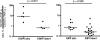
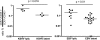
Similar articles
-
Distinct patterns of viral antigen expression in Epstein-Barr virus and Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus coinfected body-cavity-based lymphoma cell lines: potential switches in latent gene expression due to coinfection.Virology. 1999 Sep 15;262(1):18-30. doi: 10.1006/viro.1999.9876. Virology. 1999. PMID: 10489337
-
Manipulation of the immune response by Epstein-Barr virus and Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus: consequences for tumor development.Semin Cancer Biol. 2008 Dec;18(6):379-80. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2008.10.010. Epub 2008 Oct 31. Semin Cancer Biol. 2008. PMID: 18992819 No abstract available.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-specific immune reconstitution and antiviral effect of combined HAART/chemotherapy in HIV clade C-infected individuals with Kaposi's sarcoma.AIDS. 2007 Jun 19;21(10):1245-52. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e328182df03. AIDS. 2007. PMID: 17545700 Clinical Trial.
-
CD8+ T cell immunity to Epstein-Barr virus and Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpes virus.Semin Cancer Biol. 2008 Dec;18(6):416-22. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2008.10.005. Epub 2008 Nov 1. Semin Cancer Biol. 2008. PMID: 19007888 Review.
-
Molecular biology of Epstein-Barr virus and Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus.Semin Hematol. 2003 Apr;40(2):107-15. doi: 10.1053/shem.2003.50011. Semin Hematol. 2003. PMID: 12704587 Review.
Cited by
-
Generation of HIV-1-specific CD8+ cell responses following allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation.Blood. 2008 Oct 15;112(8):3484-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-05-157511. Epub 2008 Aug 12. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18698002 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
HLA class I supertypes: a revised and updated classification.BMC Immunol. 2008 Jan 22;9:1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-9-1. BMC Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18211710 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive immune responses to Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus.Curr Opin Immunol. 2022 Aug;77:102230. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2022.102230. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Curr Opin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35810680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded viral IRF3 modulates major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) antigen presentation through MHC-II transactivator-dependent and -independent mechanisms: implications for oncogenesis.J Virol. 2013 May;87(10):5340-50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00250-13. Epub 2013 Feb 28. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23449805 Free PMC article.
-
Monofunctional and polyfunctional CD8+ T cell responses to human herpesvirus 8 lytic and latency proteins.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2010 Oct;17(10):1507-16. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00189-10. Epub 2010 Aug 18. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20719985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altfeld, M., M. M. Addo, R. Shankarappa, P. K. Lee, T. M. Allen, X. G. Yu, A. Rathod, J. Harlow, K. O'Sullivan, M. N. Johnston, P. J. Goulder, J. I. Mullins, E. S. Rosenberg, C. Brander, B. Korber, and B. D. Walker. 2003. Enhanced detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific T-cell responses to highly variable regions by using peptides based on autologous virus sequences. J. Virol. 77:7330-7340. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antman, K., and Y. Chang. 2000. Kaposi's sarcoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 342:1027-1038. - PubMed
-
- Betts, M. R., J. M. Brenchley, D. A. Price, S. C. De Rosa, D. C. Douek, M. Roederer, and R. A. Koup. 2003. Sensitive and viable identification of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells by a flow cytometric assay for degranulation. J. Immunol. Methods 281:65-78. - PubMed
-
- Betts, M. R., D. A. Price, J. M. Brenchley, K. Lore, F. J. Guenaga, A. Smed-Sorensen, D. R. Ambrozak, S. A. Migueles, M. Connors, M. Roederer, D. C. Douek, and R. A. Koup. 2004. The functional profile of primary human antiviral CD8+ T cell effector activity is dictated by cognate peptide concentration. J. Immunol. 172:6407-6417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

