Association between methicillin susceptibility and biofilm regulation in Staphylococcus aureus isolates from device-related infections
- PMID: 17329452
- PMCID: PMC1865887
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02280-06
Association between methicillin susceptibility and biofilm regulation in Staphylococcus aureus isolates from device-related infections
Abstract
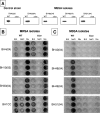
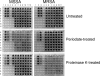
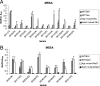
Production of icaADBC-encoded polysaccharide intercellular adhesin, or poly-N-acetylglucosamine (PIA/PNAG), represents an important biofilm mechanism in staphylococci. We previously described a glucose-induced, ica-independent biofilm mechanism in four methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolates. Here, biofilm regulation by NaCl and glucose was characterized in 114 MRSA and 98 methicillin-sensitive S. aureus (MSSA) isolates from diagnosed device-related infections. NaCl-induced biofilm development was significantly more prevalent among MSSA than MRSA isolates, and this association was independent of the isolate's genetic background as assessed by spa sequence typing. Among MSSA isolates, PIA/PNAG production correlated with biofilm development in NaCl, whereas in MRSA isolates grown in NaCl or glucose, PIA/PNAG production was not detected even though icaADBC was transcribed and regulated. Glucose-induced biofilm in MRSA was ica independent and apparently mediated by a protein adhesin(s). Experiments performed with strains that were amenable to genetic manipulation revealed that deletion of icaADBC had no effect on biofilm in a further six MRSA isolates but abolished biofilm in four MSSA isolates. Mutation of sarA abolished biofilm in seven MRSA and eight MSSA isolates. In contrast, mutation of agr in 13 MRSA and 8 MSSA isolates substantially increased biofilm (more than twofold) in only 5 of 21 (23%) isolates and had no significant impact on biofilm in the remaining 16 isolates. We conclude that biofilm development in MRSA is ica independent and involves a protein adhesin(s) regulated by SarA and Agr, whereas SarA-regulated PIA/PNAG plays a more important role in MSSA biofilm development.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Methicillin resistance and the biofilm phenotype in Staphylococcus aureus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 Jan 28;5:1. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00001. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25674541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methicillin resistance alters the biofilm phenotype and attenuates virulence in Staphylococcus aureus device-associated infections.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(4):e1002626. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002626. Epub 2012 Apr 5. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22496652 Free PMC article.
-
Biofilm formation and dispersal of Staphylococcus aureus under the influence of oxacillin.Microb Pathog. 2013 Aug-Sep;61-62:66-72. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 May 25. Microb Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23711963
-
Evidence for icaADBC-independent biofilm development mechanism in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Apr;43(4):1973-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.4.1973-1976.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15815035 Free PMC article.
-
Polysaccharide intercellular adhesin in biofilm: structural and regulatory aspects.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 Feb 10;5:7. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00007. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25713785 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Staphylococcus aureus infections: epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015 Jul;28(3):603-61. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00134-14. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26016486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of combined vancomycin and fosfomycin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in biofilms in vivo.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 31;9(12):e113133. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113133. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25551618 Free PMC article.
-
Small Molecules Produced by Commensal Staphylococcus epidermidis Disrupt Formation of Biofilms by Staphylococcus aureus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020 Feb 18;86(5):e02539-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02539-19. Print 2020 Feb 18. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31862721 Free PMC article.
-
Biofilm Formation by Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates is Differentially Affected by Glucose and Sodium Chloride Supplemented Culture Media.J Clin Med. 2019 Nov 2;8(11):1853. doi: 10.3390/jcm8111853. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31684101 Free PMC article.
-
Human monoclonal antibodies against Staphylococcus aureus surface antigens recognize in vitro and in vivo biofilm.Elife. 2022 Jan 6;11:e67301. doi: 10.7554/eLife.67301. Elife. 2022. PMID: 34989676 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

