The Pafah1b complex interacts with the reelin receptor VLDLR
- PMID: 17330141
- PMCID: PMC1800349
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000252
The Pafah1b complex interacts with the reelin receptor VLDLR
Abstract
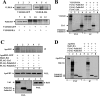
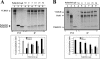
Reelin is an extracellular protein that directs the organization of cortical structures of the brain through the activation of two receptors, the very low-density lipoprotein receptor (VLDLR) and the apolipoprotein E receptor 2 (ApoER2), and the phosphorylation of Disabled-1 (Dab1). Lis1, the product of the Pafah1b1 gene, is a component of the brain platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase 1b (Pafah1b) complex, and binds to phosphorylated Dab1 in response to Reelin. Here we investigated the involvement of the whole Pafah1b complex in Reelin signaling and cortical layer formation and found that catalytic subunits of the Pafah1b complex, Pafah1b2 and Pafah1b3, specifically bind to the NPxYL sequence of VLDLR, but not to ApoER2. Compound Pafah1b1(+/-);Apoer2(-/-) mutant mice exhibit a reeler-like phenotype in the forebrain consisting of the inversion of cortical layers and hippocampal disorganization, whereas double Pafah1b1(+/-);Vldlr(-/-) mutants do not. These results suggest that a cross-talk between the Pafah1b complex and Reelin occurs downstream of the VLDLR receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Reiner O, Carrozzo R, Shen Y, Wehnert M, Faustinella F, et al. Isolation of a Miller-Dieker lissencephaly gene containing G protein beta-subunit-like repeats. Nature. 1993;364:717–721. - PubMed
-
- Hong SE, Shugart YY, Huang DT, Al Shahwan S, Grant PE, et al. Autosomal recessive lissencephaly with cerebellar hypoplasia is associated with human RELN mutations. Nature Genet. 2000;26:93–96. - PubMed
-
- Rice DS, Curran T. Role of the Reelin signaling pathway in central nervous system development. Ann Rev Neurosci. 2001;24:1005–1039. - PubMed
-
- Tissir F, Goffinet AM. Reelin and brain development. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4:496–505. - PubMed
-
- D'Arcangelo G. The reeler mouse: anatomy of a mutant. In: Dhossche DM, editor. International Review of Neurobiology. San Diego, CA: Elsevier Inc; 2005. pp. 383–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

