Tentative mapping of transcription-induced interchromosomal interaction using chimeric EST and mRNA data
- PMID: 17330142
- PMCID: PMC1804257
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000254
Tentative mapping of transcription-induced interchromosomal interaction using chimeric EST and mRNA data
Abstract
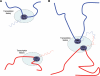
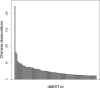
Recent studies on chromosome conformation show that chromosomes colocalize in the nucleus, bringing together active genes in transcription factories. This spatial proximity of actively transcribing genes could provide a means for RNA interaction at the transcript level. We have screened public databases for chimeric EST and mRNA sequences with the intent of mapping transcription-induced interchromosomal interactions. We suggest that chimeric transcripts may be the result of close encounters of active genes, either as functional products or "noise" in the transcription process, and that they could be used as probes for chromosome interactions. We have found a total of 5,614 chimeric ESTs and 587 chimeric mRNAs that meet our selection criteria. Due to their higher quality, the mRNA findings are of particular interest and we hope that they may serve as food for thought for specialists in diverse areas of molecular biology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Johnson J, Castle J, Garrett-Engele P, Kan Z, Loerch P, et al. Genome-wide survey of human alternative pre-mRNA splicing with exon junction microarrays. Science. 2003;302:2141–4. - PubMed
-
- Yelin R, Dahary D, Sorek R, Levanon E, Goldstein O, et al. Widespread occurrence of antisense transcription in the human genome. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21:379–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

