Sialoadhesin (CD169) expression in CD14+ cells is upregulated early after HIV-1 infection and increases during disease progression
- PMID: 17330143
- PMCID: PMC1804103
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000257
Sialoadhesin (CD169) expression in CD14+ cells is upregulated early after HIV-1 infection and increases during disease progression
Abstract
Background: Sialoadhesin (CD169, siglec-1 or Sn) is an activation marker seen on macrophages in chronic inflammatory diseases and in tumours, and on subsets of tissue macrophages. CD169 is highly expressed by macrophages present in AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma lesions. It is also increased on blood monocytes of HIV-1 infected patients with a high viral load despite antiretroviral treatment.
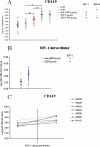
Methodology/principal findings: We investigated expression of sialoadhesin in untreated HIV-1 and HHV-8 infected patients, by real-time PCR and FACS analysis to establish its expression in relation to infection and disease progression. Patients analysed were either HIV-1 seroconverters (n = 7), in the chronic phase of HIV-1 infection (n = 21), or in the AIDS stage (n = 58). Controls were HHV-8 infected, but otherwise healthy individuals (n = 20), and uninfected men having sex with men (n = 24). Sialoadhesin mRNA was significantly elevated after HIV-1, but not HHV-8 infection, and a further increase was seen in AIDS patients. Samples obtained around HIV-1 seroconversion indicated that sialoadhesin levels go up early in infection. FACS analysis of PBMCs showed that sialoadhesin protein was expressed at high levels by approximately 90% of CD14(+) and CD14(+)CD16(+)cells of HIV-1(+) patients with a concomitant 10-fold increase in sialoadhesin protein/cell compared with uninfected controls.
Conclusions/significance: We have shown that sialoadhesin is induced to high levels on CD14(+) cells early after HIV-1 infection in vivo. The phenotype of the cells is maintained during disease progression, suggesting that it could serve as a marker for infection and probably contributes to the severe dysregulation of the immune system seen in AIDS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Decrion AZ, Dichamp I, Varin A, Herbein G. HIV and inflammation. Curr HIV Res. 2005;3:243–259. - PubMed
-
- Hartnell A, Steel J, Turley H, Jones M, Jackson DG, et al. Characterization of human sialoadhesin, a sialic acid binding receptor expressed by resident and inflammatory macrophage populations. Blood. 2001;97:288–296. - PubMed
-
- Pulliam L, Sun B, Rempel H. Invasive chronic inflammatory monocyte phenotype in subjects with high HIV-1 viral load. J Neuroimmunol. 2004;157:93–98. - PubMed
-
- Kirchberger S, Majdic O, Steinberger P, Bluml S, Pfistershammer K, et al. Human rhinoviruses inhibit the accessory function of dendritic cells by inducing sialoadhesin and B7-H1 expression. J Immunol. 2005;175:1145–1152. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

