Progesterone reduces erectile dysfunction in sleep-deprived spontaneously hypertensive rats
- PMID: 17331246
- PMCID: PMC1821029
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7827-5-7
Progesterone reduces erectile dysfunction in sleep-deprived spontaneously hypertensive rats
Abstract
Background: Paradoxical sleep deprivation (PSD) associated with cocaine has been shown to enhance genital reflexes (penile erection-PE and ejaculation-EJ) in Wistar rats. Since hypertension predisposes males to erectile dysfunction, the aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of PSD on genital reflexes in the spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR) compared to the Wistar strain. We also extended our study to examine how PSD affect steroid hormone concentrations involved in genital events in both experimental models.
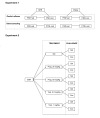
Methods: The first experiment investigated the effects of PSD on genital reflexes of Wistar and SHR rats challenged by saline and cocaine (n = 10/group). To further examine the impact of the PSD on concentrations of sexual hormones, we performed a hormonal analysis of testosterone and progesterone in the Wistar and in SHR strains. Since after PSD progesterone concentrations decreased in the SHR compared to the Wistar PSD group we extended our study by investigating whether progesterone (25 mg/kg or 50 mg/kg) or testosterone (0.5 mg/kg or 1.0 mg/kg) administration during PSD would have a facilitator effect on the occurrence of genital reflexes in this hypertensive strain.
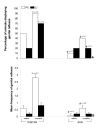
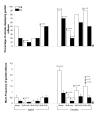
Results: A 4-day period of PSD induced PE in 50% of the Wistar rats against 10% for the SHR. These genital reflexes was potentiated by cocaine in Wistar rats whereas this scenario did not promote significant enhancement in PE and EJ in hypertensive rats, and the percentage of SHR displaying genital reflexes still figured significantly lower than that of the Wistar strain. As for hormone concentrations, both sleep-deprived Wistar and SHR showed lower testosterone concentrations than their respective controls. Sleep deprivation promoted an increase in concentrations of progesterone in Wistar rats, whereas no significant alterations were found after PSD in the SHR strain, which did not present enhancement in erectile responses. In order to explore the role of progesterone in the occurrence of genital reflexes, SHR were treated daily during the sleep deprivation period with progesterone; after the administration of this hormone and challenge with cocaine, we observed a significant increase in erectile events compared with the vehicle PSD SHR+cocaine group.
Conclusion: Our data showed that the low frequency of genital reflexes found in SHR sleep deprived rats may be attributed to the lower concentrations of progesterone in these rats, based on the observation that progesterone replacement increased genital reflexes in this strain.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of paradoxical sleep deprivation on genital reflexes in five rat strains.Horm Behav. 2006 Feb;49(2):173-80. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2005.05.021. Epub 2005 Jul 11. Horm Behav. 2006. PMID: 16005458
-
Diurnal variation in the genital reflexes and hormone levels induced by paradoxical sleep deprivation and cocaine in male rats.Brain Res Bull. 2004 Sep 30;64(3):215-20. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2004.07.007. Brain Res Bull. 2004. PMID: 15464857
-
Effects of progesterone blockade over cocaine-induced genital reflexes of paradoxical sleep-deprived male rats.Horm Behav. 2005 Apr;47(4):477-84. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2004.12.005. Horm Behav. 2005. PMID: 15777814
-
The effects of testosterone on sleep and sleep-disordered breathing in men: its bidirectional interaction with erectile function.Sleep Med Rev. 2008 Oct;12(5):365-79. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2007.12.003. Epub 2008 Jun 5. Sleep Med Rev. 2008. PMID: 18519168 Review.
-
Sexual function in altered physiological states: comparison of effects of hypertension, diabetes, hyperprolactinemia, and others to "normal" aging in male rats.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1995 Summer;19(2):279-302. doi: 10.1016/0149-7634(94)00058-9. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1995. PMID: 7630583 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of androgen deprivation therapy on sexual function.Asian J Androl. 2012 Mar;14(2):198-203. doi: 10.1038/aja.2011.106. Epub 2012 Jan 9. Asian J Androl. 2012. PMID: 22231298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psychobiological Protective Factors Modifying the Association Between Age and Sexual Health in Men: Findings From the Men's Health 40+ Study.Am J Mens Health. 2017 May;11(3):737-747. doi: 10.1177/1557988316689238. Epub 2017 Feb 13. Am J Mens Health. 2017. PMID: 28413941 Free PMC article.
-
Male fertility is reduced by chronic intermittent hypoxia mimicking sleep apnea in mice.Sleep. 2014 Nov 1;37(11):1757-65. doi: 10.5665/sleep.4166. Sleep. 2014. PMID: 25364071 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Doumas M, Tsakiris A, Douma S, Grigorakis A, Papadopoulos A, Hounta A, Tsiodras S, Dimitriou D, Giamarellou H. Factors affecting the increased prevalence of erectile dysfunction in Greek hypertensive compared with normotensive subjects. J Androl. 2006;27:469–477. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.04191. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Clark JT, Sahu A, Mrotek JJ, Kalra SP. Sexual function and neuropeptide Y levels in selected brain regions in male spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol. 1991;261:R1234–1241. - PubMed
-
- Clark JT, Smith ER, Davidson JM. Evidence for the modulation of sexual behavior by α-adrenoceptors in male rats. Neuroendocrinol. 1985;41:36–43. - PubMed
-
- Tufik S, Lindsey CJ, Carlini EA. Does REM sleep deprivation induce a supersensitivity of dopaminergic receptors in the rat brain? Pharmacol. 1978;16:95–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

