Strain-specific steroidal control of pituitary function
- PMID: 17332521
- PMCID: PMC4727746
- DOI: 10.1677/JOE-06-0145
Strain-specific steroidal control of pituitary function
Abstract
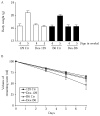
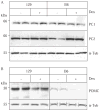
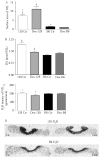
We have previously shown that 7B2 null mice on the 129/SvEvTac (129) genetic background die at 5 weeks of age with hypercorticosteronemia due to a Cushing's-like disease unless they are rescued by adrenalectomy; however, 7B2 nulls on the C57BL/6NTac (B6) background remain healthy, with normal steroid levels. Since background exerts such a profound influence on the phenotype of this mutation, we have evaluated whether these two different mouse strains respond differently to high circulating steroids by chronically treating wild-type 129 and B6 mice with the synthetic steroid dexamethasone (Dex). Dex treatment decreased the dopamine content of the neurointermediate lobes (NIL) of 129 mice, leading to NIL enlargement and increased total D(2)R mRNA in the 129, but not the B6, NIL. Despite the decrease in this inhibitory transmitter, Dex-treated 129 mice exhibited reduced circulating alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH) along with reduced POMC-derived peptides compared with controls, possibly due to reduced POMC content in the NIL. In contrast, Dex-treated B6 mice showed lowered cellular ACTH, unchanged alpha-MSH and beta-endorphin, and increased circulating alpha-MSH, most likely due to increased cleavage of NIL ACTH by increased PC2. Dex-treated 129 mice exhibited hyperinsulinemia and lowered blood glucose, whereas Dex-treated B6 mice showed slightly increased glucose levels despite their considerably increased insulin levels. Taken together, our results suggest that the endocrinological response of 129 mice to chronic Dex treatment is very different from that of B6 mice. These strain-dependent differences in steroid sensitivity must be taken into account when comparing different lines of transgenic or knockout mice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that would prejudice the impartiality of this scientific work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mortality in 7B2 null mice can be rescued by adrenalectomy: involvement of dopamine in ACTH hypersecretion.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Mar 5;99(5):3087-92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.261715099. Epub 2002 Feb 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11854475 Free PMC article.
-
Strain-dependent influences on the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis profoundly affect the 7B2 and PC2 null phenotypes.Endocrinology. 2005 Aug;146(8):3438-44. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-1289. Epub 2005 May 5. Endocrinology. 2005. PMID: 15878971
-
Concomitant dopaminergic and glucocorticoid control of pituitary proopiomelanocortin messenger ribonucleic acid and beta-endorphin levels.Endocrinology. 1987 Nov;121(5):1689-96. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-5-1689. Endocrinology. 1987. PMID: 2959468
-
Absence of dopaminergic control on melanotrophs leads to Cushing's-like syndrome in mice.Mol Endocrinol. 1998 Aug;12(8):1133-9. doi: 10.1210/mend.12.8.0144. Mol Endocrinol. 1998. PMID: 9717839
-
Ontogeny of basal and regulated proopiomelanocortin-derived peptide secretion from fetal and neonatal pituitary intermediate lobe cells: melanotrophs exhibit transient glucocorticoid responses during development.Dev Biol. 1996 Jan 10;173(1):110-8. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1996.0010. Dev Biol. 1996. PMID: 8575613
Cited by
-
Minireview: new molecular mediators of glucocorticoid receptor activity in metabolic tissues.Mol Endocrinol. 2014 Jul;28(7):999-1011. doi: 10.1210/me.2014-1062. Epub 2014 Apr 25. Mol Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24766141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of corticosterone on sleep homeostasis induced by REM sleep deprivation in rats.PLoS One. 2013 May 7;8(5):e63520. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063520. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23667630 Free PMC article.
-
Methadone-induced hypoglycemia.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2013 May;33(4):537-42. doi: 10.1007/s10571-013-9919-6. Epub 2013 Mar 7. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23467779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antakly T, Mercille S, Cote JP. Tissue-specific dopaminergic regulation of the glucocorticoid receptor in the rat pituitary. Endocrinology. 1987;120:1558–1562. - PubMed
-
- Autelitano DJ, Clements JA, Nikolaidis I, Canny BJ, Funder JW. Concomitant dopaminergic and glucocorticoid control of pituitary proopiomelanocortin messenger ribonucleic acid and beta-endorphin levels. Endocrinology. 1987;121:1689–1696. - PubMed
-
- Autelitano DJ, Snyder L, Sealfon SC, Roberts JL. Dopamine D2-receptor messenger RNA is differentially regulated by dopaminergic agents in rat anterior and neurointermediate pituitary. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. 1989;67:101–105. - PubMed
-
- Barbero P, Kitabgi P. Protein 7B2 is essential for the targeting and activation of PC2 into the regulated secretory pathway of rMTC 6–23 cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 1999;257:473–479. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu M, Goldman ME, Miyazaki K, Frey EA, Eskay RL, Kebabian JW, Cote TE. Bromocriptine-induced changes in the biochemistry, physiology, and histology of the intermediate lobe of the rat pituitary gland. Endocrinology. 1984;114:1871–1884. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

