Shotgun proteomics implicates protease inhibition and complement activation in the antiinflammatory properties of HDL
- PMID: 17332893
- PMCID: PMC1804352
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI26206
Shotgun proteomics implicates protease inhibition and complement activation in the antiinflammatory properties of HDL
Abstract
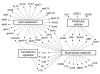
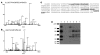
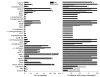
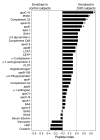
HDL lowers the risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease by promoting cholesterol efflux from macrophage foam cells. However, other antiatherosclerotic properties of HDL are poorly understood. To test the hypothesis that the lipoprotein carries proteins that might have novel cardioprotective activities, we used shotgun proteomics to investigate the composition of HDL isolated from healthy subjects and subjects with coronary artery disease (CAD). Unexpectedly, our analytical strategy identified multiple complement-regulatory proteins and a diverse array of distinct serpins with serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity. Many acute-phase response proteins were also detected, supporting the proposal that HDL is of central importance in inflammation. Mass spectrometry and biochemical analyses demonstrated that HDL3 from subjects with CAD was selectively enriched in apoE, raising the possibility that HDL carries a unique cargo of proteins in humans with clinically significant cardiovascular disease. Collectively, our observations suggest that HDL plays previously unsuspected roles in regulating the complement system and protecting tissue from proteolysis and that the protein cargo of HDL contributes to its antiinflammatory and antiatherogenic properties.
Figures

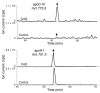
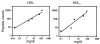
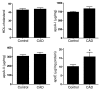
Comment in
-
HDL proteomics: pot of gold or Pandora's box?J Clin Invest. 2007 Mar;117(3):595-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI31608. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17332889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braunwald E. Cardiovascular medicine at the turn of the millennium: triumphs, concerns, and opportunities. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997;337:1360–1369. - PubMed
-
- Hoyert D.L., Kung H.-C., Smith B.L. Deaths: preliminary data for 2003. Natl. Vital Stat. Rep. 2005;53:1–48. - PubMed
-
- Gordon D.J., Rifkind B.M. High-density lipoprotein — the clinical implications of recent studies. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989;321:1311–1316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01HL030086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL030086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK02456/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL57557/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL078527/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30ES07033/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL057557/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL078527/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086798/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES007033/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HL086798/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL074223/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK002456/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL074223/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

