Protection against inhaled oxidants through scavenging of oxidized lipids by macrophage receptors MARCO and SR-AI/II
- PMID: 17332894
- PMCID: PMC1804372
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI29968
Protection against inhaled oxidants through scavenging of oxidized lipids by macrophage receptors MARCO and SR-AI/II
Abstract
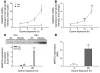
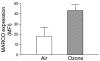
Alveolar macrophages (AMs) express the class A scavenger receptors (SRAs) macrophage receptor with collagenous structure (MARCO) and scavenger receptor AI/II (SRA-I/II), which recognize oxidized lipids and provide innate defense against inhaled pathogens and particles. Increased MARCO expression in lungs of ozone-resistant mice suggested an additional role protecting against inhaled oxidants. After ozone exposure, MARCO-/- mice showed greater lung injury than did MARCO+/+ mice. Ozone is known to generate oxidized, proinflammatory lipids in lung lining fluid, such as 5beta,6beta-epoxycholesterol (beta-epoxide) and 1-palmitoyl-2-(9'-oxo-nonanoyl)-glycerophosphocholine (PON-GPC). Intratracheal instillation of either lipid caused substantial neutrophil influx in MARCO-/- mice, but had no effect in MARCO+/+ mice. Normal AMs showed greater uptake in vitro of beta-epoxide compared with MARCO-/- AMs, consistent with SRA function in binding oxidized lipids. SR-AI/II-/- mice showed similar enhanced acute lung inflammation after beta-epoxide or another inhaled oxidant (aerosolized leachate of residual oil fly ash). In contrast, subacute ozone exposure did not enhance inflammation in SR-AI/II-/- versus SR-AI/II+/+ mice, reflecting increased AM expression of MARCO. These data identify what we believe to be a novel function for AM SRAs in decreasing pulmonary inflammation after oxidant inhalation by scavenging proinflammatory oxidized lipids from lung lining fluids.
Figures

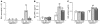
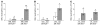
Comment in
-
Scavenger receptors clear the air.J Clin Invest. 2007 Mar;117(3):601-4. doi: 10.1172/JCI31549. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17332891 Free PMC article.
References
-
- MacNee W., Rahman I. Is oxidative stress central to the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease? Trends Mol. Med. 2001;7:55–62. - PubMed
-
- Bowler R.P. Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of asthma. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2004;4:116–122. - PubMed
-
- Mudway I.S., Kelly F.J. Ozone and the lung: a sensitive issue. Mol. Aspects Med. 2000;21:1–48. - PubMed
-
- Pulfer M.K., Murphy R.C. Formation of biologically active oxysterols during ozonolysis of cholesterol present in lung surfactant. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:26331–26338. - PubMed
-
- Uhlson C., et al. Oxidized phospholipids derived from ozone-treated lung surfactant extract reduce macrophage and epithelial cell viability. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2002;15:896–906. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

