Using improved technology for filter paper-based blood collection to survey wild Sika deer for antibodies to hepatitis E virus
- PMID: 17336401
- PMCID: PMC2770239
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2007.01.016
Using improved technology for filter paper-based blood collection to survey wild Sika deer for antibodies to hepatitis E virus
Abstract
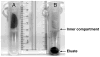
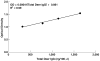
Recent reports from Japan implicated wild Sika deer (Cervus nippon) in the zoonotic transmission of hepatitis E to humans. Seroprevalence studies were performed to determine if imported feral populations of Sika deer in Maryland and Virginia posed a similar risk of transmitting hepatitis E virus (HEV). Hunters collected blood on filter paper discs from freshly killed deer. The discs were desiccated and delivered to a collection point. The dried filters were weighed to estimate the amount of blood absorbed and were eluted and collected in one tube via a novel extraction system. The procedure was quantified and validated with negative and positive serum and blood samples obtained from domestic Sika deer before and after immunization with HEV recombinant capsid protein, respectively. None of the 155 tested samples contained antibody to HEV, suggesting that Sika deer in these populations, unlike those in Japan, do not pose a significant zoonotic threat for hepatitis E. However, the new method developed for collecting and eluting the samples should prove useful for field studies of many other pathogens.
Figures


References
-
- Arankalle VA, Tsarev SA, Chadha MS, Alling DW, Emerson SU, Banerjee K, Purcell RH. Age-specific prevalence of antibodies to hepatitis A and E viruses in Pune, India, 1982 and 1992. J Infect Dis. 1995;171:447–450. - PubMed
-
- De Swart RL, Nur Y, Abdallah A, Kruining H, El Mubarak HS, Ibrahim SA, Van Den Hoogen B, Groen J, Osterhaus AD. Combination of reverse transcriptase PCR analysis and immunoglobulin M detection on filter paper blood samples allows diagnostic and epidemiological studies of measles. J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39:270–273. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Emerson SU, Anderson D, Arankalle A, Meng X-J, Purdy M, Schlauder GG, Tsarev SA. Herpesvirus. Virus taxonomy, VIIth Report of the ICTV. 2004:851–855.
-
- Emerson SU, Clemente-Casares P, Moiduddin N, Arankalle VA, Torian U, Purcell RH. Putative neutralization epitopes and broad cross-genotype neutralization of Hepatitis E virus confirmed by a quantitative cell-culture assay. J Gen Virol. 2006;87:697–704. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

