Multi-tasking on chromatin with the SAGA coactivator complexes
- PMID: 17337012
- PMCID: PMC1892243
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2006.09.008
Multi-tasking on chromatin with the SAGA coactivator complexes
Abstract
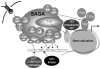
Over the past 10 years, much progress has been made to understand the roles of the similar, yet distinct yeast SAGA and SLIK coactivator complexes involved in histone post-translational modification and gene regulation. Many different groups have elucidated functions of the SAGA complexes including identification of novel components, which have conferred additional distinct functions. Together, recent studies demonstrate unique attributes of the SAGA coactivator complexes in histone acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, and deubiquitination. In addition to roles in transcriptional activation with the 19S proteasome regulatory particle, recent evidence also suggests functions for SAGA in elongation and mRNA export. The modular nature of SAGA allows this approximately 1.8 MDa complex to organize its functions and carry out multiple roles during transcription, particularly under conditions of cellular stress.
Figures

References
-
- Felsenfeld G, Groudine M. Controlling the double helix. Nature. 2003;421:448–453. - PubMed
-
- Kornberg RD. Chromatin structure: a repeating unit of histones and DNA. Science. 1974;184:868–871. - PubMed
-
- Luger K. Structure and dynamic behavior of nucleosomes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2003;13:127–135. - PubMed
-
- Workman JL, Kingston RE. Alteration of nucleosome structure as a mechanism of transcriptional regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:545–579. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

