Lack of control of nitrite assimilation by ammonium in an oceanic picocyanobacterium, Synechococcus sp. strain WH 8103
- PMID: 17337543
- PMCID: PMC1892888
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02606-06
Lack of control of nitrite assimilation by ammonium in an oceanic picocyanobacterium, Synechococcus sp. strain WH 8103
Abstract
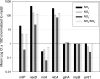
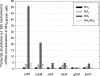
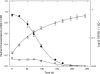
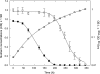
In cyanobacteria, the transcriptional activator NtcA is involved in global nitrogen control and, in the absence of ammonium, regulates the expression of genes involved in the assimilation of alternative nitrogen sources. The oceanic picocyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain WH 8103 harbors a copy of ntcA, but in the present study, we show that unlike other marine cyanobacteria that have been investigated, this strain is capable of coassimilating nitrite when grown in the presence of ammonium. Transcript levels for the genes encoding the nitrate/nitrite-bispecific permease NrtP and nitrate reductase (NarB) were substantially down-regulated by ammonium, whereas the abundances of nitrite reductase (NirA) transcripts were similar in nitrite- and ammonium-grown cells. The growth of Synechococcus sp. strain WH 8103 in medium containing both ammonium and nitrite resulted in only minor changes in the expression profile in comparison to that of nitrite-grown cells with the exception that the gene encoding the high-affinity ammonium transporter Amt1 was down-regulated to the levels seen in ammonium-grown cells. Whereas the expression of nrtP, narB, and amt1 appears to be NtcA dependent in this marine cyanobacterium, the transcription and expression of nirA appear not to be. The ability to coassimilate nitrite and reduced-nitrogen sources like ammonium may be an adaptive trait that enables oceanic strains like Synechococcus sp. strain WH 8103 to exploit the low nitrite concentrations found in oceanic surface waters that are not available to their principal and more numerous competitor, Prochlorococcus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nitrate/nitrite assimilation system of the marine picoplanktonic cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain WH 8103: effect of nitrogen source and availability on gene expression.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003 Dec;69(12):7009-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.12.7009-7018.2003. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 14660343 Free PMC article.
-
A novel nitrate/nitrite permease in the marine Cyanobacterium synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7002.J Bacteriol. 1999 Dec;181(23):7363-72. doi: 10.1128/JB.181.23.7363-7372.1999. J Bacteriol. 1999. PMID: 10572142 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of ntcA expression and nitrite uptake in the marine Synechococcus sp. strain WH 7803.J Bacteriol. 1998 Apr;180(7):1878-86. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.7.1878-1886.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9537388 Free PMC article.
-
Photosynthetic nitrate assimilation in cyanobacteria.Photosynth Res. 2005;83(2):117-33. doi: 10.1007/s11120-004-5830-9. Photosynth Res. 2005. PMID: 16143847 Review.
-
Regulation of nitrate assimilation in cyanobacteria.J Exp Bot. 2011 Feb;62(4):1411-24. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq427. Epub 2011 Jan 31. J Exp Bot. 2011. PMID: 21282331 Review.
Cited by
-
Marine Synechococcus sp. Strain WH7803 Shows Specific Adaptative Responses to Assimilate Nanomolar Concentrations of Nitrate.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0018722. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00187-22. Epub 2022 Jul 19. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35852322 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of bacterial communities along the spatial and environmental gradients from Bohai Sea to northern Yellow Sea.PeerJ. 2018 Jan 29;6:e4272. doi: 10.7717/peerj.4272. eCollection 2018. PeerJ. 2018. PMID: 29404208 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological Studies of Glutamine Synthetases I and III from Synechococcus sp. WH7803 Reveal Differential Regulation.Front Microbiol. 2016 Jun 28;7:969. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00969. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27446010 Free PMC article.
-
Upward nitrate transport by phytoplankton in oceanic waters: balancing nutrient budgets in oligotrophic seas.PeerJ. 2014 Mar 13;2:e302. doi: 10.7717/peerj.302. eCollection 2014. PeerJ. 2014. PMID: 24688877 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal orchestration of glycogen synthase (GlgA) gene expression and glycogen accumulation in the oceanic picoplanktonic cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain WH8103.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Jul;78(13):4744-7. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00254-12. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22522678 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brzezinski, M. A. 1988. Vertical distributions of ammonium in stratified oligotrophic waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 33:1176-1182.
-
- Chisolm, S. W., R. J. Olson, E. R. Zettler, R. Goericke, J. B. Waterbury, and N. A. Welschmeyer. 1988. A novel free-living prochlorophyte abundant in the oceanic euphotic zone. Nature 334:340-343.
-
- Flores, E., and A. Herrero. 1994. Assimilatory nitrogen metabolism and its regulation, p. 487-517. In D. A. Bryant (ed.), The molecular biology of cyanobacteria. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

