Dynamics of genomic-library enrichment and identification of solvent tolerance genes for Clostridium acetobutylicum
- PMID: 17337545
- PMCID: PMC1892849
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02296-06
Dynamics of genomic-library enrichment and identification of solvent tolerance genes for Clostridium acetobutylicum
Abstract
A Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824 genomic library was constructed using randomly sheared DNA. Library inserts conferring increased tolerance to 1-butanol were isolated using two protocols. Protocol I utilized a single round of butanol challenges in batch culture, while protocol II, which gave clearly superior outcomes, was based on the serial transfer of stationary-phase cultures into progressively higher butanol concentrations. DNA microarray analysis made a high-resolution assessment of the dynamic process of library enrichment possible for the first time. Protocol I yielded a library insert containing the entire coding region of the gene CAC0003 (which codes for a protein of unknown function) but also several DNA fragments containing promoter regions. Protocol II enabled the successful identification of DNA fragments containing several intact genes conferring preferential growth under conditions of butanol stress. Since expression using the employed library is possible only from natural promoters, among the enriched genes, we identified 16 genes that constitute the first cistron of a transcriptional unit. These genes include four transcriptional regulators (CAC0977, CAC1463, CAC1869, and CAC2495). After subcloning plasmids carrying the CAC0003 and CAC1869 genes, strains 824(pCAC0003) and 824(pCAC1869) exhibited 13% and an 81% increases, respectively, in butanol tolerance relative to the plasmid control strain. 824(pCAC1869) consistently grew to higher cell densities in challenged and unchallenged cultures and exhibited prolonged metabolism. Our serial enrichment approach provided a more detailed understanding of the dynamic process of library enrichment under conditions of selective growth. Further characterization of the genes identified in this study will likely enhance our understanding of the complex phenotype of solvent tolerance.
Figures
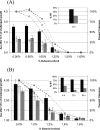
 ), 824(pIMP1) (
), 824(pIMP1) ( ), and 824(pCAC0003) (□). Growth measurements were used to calculate the percent tolerance at each challenge level for 824(pCAC1869) (□), 824(pIMP1) (○), and 824(pCAC0003) (▵). (A) Inoculation of a dilution series of butanol in CGM. (B) Butanol challenge of actively growing cultures (A600 of ∼1.0). Growth data for 12 h postchallenge are displayed. Inset graphs show the percent relative tolerance (% RT) to butanol for library strains relative to the pIMP1 control strain. See the text for details.
), and 824(pCAC0003) (□). Growth measurements were used to calculate the percent tolerance at each challenge level for 824(pCAC1869) (□), 824(pIMP1) (○), and 824(pCAC0003) (▵). (A) Inoculation of a dilution series of butanol in CGM. (B) Butanol challenge of actively growing cultures (A600 of ∼1.0). Growth data for 12 h postchallenge are displayed. Inset graphs show the percent relative tolerance (% RT) to butanol for library strains relative to the pIMP1 control strain. See the text for details.References
-
- Alper, H., J. Moxley, E. Nevoigt, G. R. Fink, and G. Stephanopoulos. 2006. Engineering yeast transcription machinery for improved ethanol tolerance and production. Science 314:1565-1568. - PubMed
-
- Alsaker, K. V. 2006. Microarray-based transcriptional analyses of stationary phase phenomena and stress responses in Clostridium acetobutylicum. Ph.D. thesis. Northwestern University, Evanston, IL.
-
- Alsaker, K. V., C. J. Paredes, and E. T. Papoutsakis. 2005. Design, optimization and validation of genomic DNA microarrays for examining the Clostridium acetobutylicum transcriptome. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 10:432-443.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

