A putative gene cluster for aminoarabinose biosynthesis is essential for Burkholderia cenocepacia viability
- PMID: 17337576
- PMCID: PMC1855895
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00153-07
A putative gene cluster for aminoarabinose biosynthesis is essential for Burkholderia cenocepacia viability
Abstract
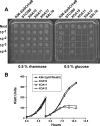
Using a conditional mutagenesis strategy we demonstrate here that a gene cluster encoding putative aminoarabinose (Ara4N) biosynthesis enzymes is essential for the viability of Burkholderia cenocepacia. Loss of viability is associated with dramatic changes in bacterial cell morphology and ultrastructure, increased permeability to propidium iodide, and sensitivity to sodium dodecyl sulfate, suggesting a general cell envelope defect caused by the lack of Ara4N.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Burkholderia cenocepacia requires a periplasmic HtrA protease for growth under thermal and osmotic stress and for survival in vivo.Infect Immun. 2007 Apr;75(4):1679-89. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01581-06. Epub 2007 Jan 12. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17220310 Free PMC article.
-
The Burkholderia cenocepacia K56-2 pleiotropic regulator Pbr, is required for stress resistance and virulence.Microb Pathog. 2010 May;48(5):168-77. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2010.02.006. Epub 2010 Mar 3. Microb Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20206249
-
Identification of essential operons with a rhamnose-inducible promoter in Burkholderia cenocepacia.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 Apr;72(4):2547-55. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.4.2547-2555.2006. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16597956 Free PMC article.
-
Aminoarabinose is essential for lipopolysaccharide export and intrinsic antimicrobial peptide resistance in Burkholderia cenocepacia(†).Mol Microbiol. 2012 Sep;85(5):962-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2012.08154.x. Epub 2012 Jul 18. Mol Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22742453
-
Burkholderia cenocepacia in cystic fibrosis: epidemiology and molecular mechanisms of virulence.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010 Jul;16(7):821-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03237.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010. PMID: 20880411 Review.
Cited by
-
A decade of Burkholderia cenocepacia virulence determinant research.Infect Immun. 2010 Oct;78(10):4088-100. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00212-10. Epub 2010 Jul 19. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20643851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the metabolic network of the epidemic pathogen Burkholderia cenocepacia J2315 via genome-scale reconstruction.BMC Syst Biol. 2011 May 25;5:83. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-5-83. BMC Syst Biol. 2011. PMID: 21609491 Free PMC article.
-
The genome of Burkholderia cenocepacia J2315, an epidemic pathogen of cystic fibrosis patients.J Bacteriol. 2009 Jan;191(1):261-77. doi: 10.1128/JB.01230-08. Epub 2008 Oct 17. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 18931103 Free PMC article.
-
The twin arginine translocation system is essential for aerobic growth and full virulence of Burkholderia thailandensis.J Bacteriol. 2014 Jan;196(2):407-16. doi: 10.1128/JB.01046-13. Epub 2013 Nov 8. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 24214943 Free PMC article.
-
Hopanoid production is required for low-pH tolerance, antimicrobial resistance, and motility in Burkholderia cenocepacia.J Bacteriol. 2011 Dec;193(23):6712-23. doi: 10.1128/JB.05979-11. Epub 2011 Sep 30. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21965564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bader, M. W., S. Sanowar, M. E. Daley, A. R. Schneider, U. Cho, W. Xu, R. E. Klevit, H. Le Moual, and S. I. Miller. 2005. Recognition of antimicrobial peptides by a bacterial sensor kinase. Cell 122:461-472. - PubMed
-
- Bailey, A. M., S. Mahapatra, P. J. Brennan, and D. C. Crick. 2002. Identification, cloning, purification, and enzymatic characterization of Mycobacterium tuberculosis 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase. Glycobiology 12:813-820. - PubMed
-
- Breazeale, S. D., A. A. Ribeiro, and C. R. Raetz. 2002. Oxidative decarboxylation of UDP-glucuronic acid in extracts of polymyxin-resistant Escherichia coli. Origin of lipid a species modified with 4-amino-4-deoxy-l-arabinose. J. Biol. Chem. 277:2886-2896. - PubMed
-
- Breazeale, S. D., A. A. Ribeiro, and C. R. H. Raetz. 2003. Origin of lipid A species modified with 4-amino-4-deoxy-l-arabinose in polymyxin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli: an aminotransferase (arnB) that generates UDP-4-amino-4-deoxy-l-arabinose. J. Biol. Chem. 278:24731-24739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

