A-factor and phosphate depletion signals are transmitted to the grixazone biosynthesis genes via the pathway-specific transcriptional activator GriR
- PMID: 17337580
- PMCID: PMC1855879
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00055-07
A-factor and phosphate depletion signals are transmitted to the grixazone biosynthesis genes via the pathway-specific transcriptional activator GriR
Abstract
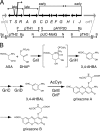
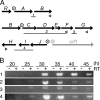
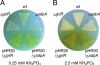
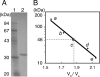
Grixazone (GX), which is a diffusible yellow pigment containing a phenoxazinone chromophore, is one of the secondary metabolites under the control of A-factor (2-isocapryloyl-3R-hydroxymethyl-gamma-butyrolactone) in Streptomyces griseus. GX production is also induced by phosphate starvation. The whole biosynthesis gene cluster for GX was cloned and characterized. The gene cluster consisting of 13 genes contained six transcriptional units, griT, griSR, griR, griAB, griCDEFG, and griJIH. During cultivation in a phosphate-depleted medium, the six promoters were activated in the order (i) griR, (ii) griC and griJ, and (iii) griT, griS, and griA. Disruption of griR, which encodes a SARP family transcriptional regulator, abolished the transcriptional activation of all other genes in the cluster. In addition, ectopic expression of griR from a constitutively active promoter resulted in GX overproduction even in the absence of AdpA, a key transcriptional activator in the A-factor regulatory cascade, and in the presence of phosphate at a high concentration. GriR monomers bound direct repeat sequences in the griC and griJ promoters in a cooperative manner. Therefore, the early active genes (griCDEFG and griJIH), all of which, except for griG (which encodes a transporter-like protein), encode the GX biosynthesis enzymes, were directly activated by GriR. The transcription of griR was greatly reduced in the presence of phosphate at a high concentration and was hardly detected in the absence of AdpA. These findings showed that both A-factor and phosphate depletion signals were required for griR transcription and both signals were transmitted to the GX biosynthesis genes solely via the griR promoter.
Figures


References
-
- Angell, S., E. Schwarz, and M. J. Bibb. 1992. The glucose kinase gene of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2): its nucleotide sequence, transcriptional analysis and role in glucose repression. Mol. Microbiol. 6:2833-2844. - PubMed
-
- Asturias, J. A., P. Liras, and J. F. Martín. 1990. Phosphate control of pabS gene transcription during candicidin biosynthesis. Gene 93:79-84. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingstone, D. O. Moore, J. S. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1987. Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, NY.
-
- Beck, E., G. Ludwig, E. A. Auerswald, B. Reiss, and H. Schaller. 1982. Nucleotide sequence and exact localization of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene from transposon Tn5. Gene 19:327-336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

