In vitro studies of the uridylylation of the three PII protein paralogs from Rhodospirillum rubrum: the transferase activity of R. rubrum GlnD is regulated by alpha-ketoglutarate and divalent cations but not by glutamine
- PMID: 17337583
- PMCID: PMC1855872
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01704-06
In vitro studies of the uridylylation of the three PII protein paralogs from Rhodospirillum rubrum: the transferase activity of R. rubrum GlnD is regulated by alpha-ketoglutarate and divalent cations but not by glutamine
Abstract
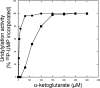
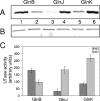
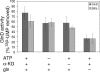
P(II) proteins have been shown to be key players in the regulation of nitrogen fixation and ammonia assimilation in bacteria. The mode by which these proteins act as signals is by being in either a form modified by UMP or the unmodified form. The modification, as well as demodification, is catalyzed by a bifunctional enzyme encoded by the glnD gene. The regulation of this enzyme is thus of central importance. In Rhodospirillum rubrum, three P(II) paralogs have been identified. In this study, we have used purified GlnD and P(II) proteins from R. rubrum, and we show that for the uridylylation activity of R. rubrum GlnD, alpha-ketoglutarate is the main signal, whereas glutamine has no effect. This is in contrast to, e.g., the Escherichia coli system. Furthermore, we show that all three P(II) proteins are uridylylated, although the efficiency is dependent on the cation present. This difference may be of importance in understanding the effects of the P(II) proteins on the different target enzymes. Furthermore, we show that the deuridylylation reaction is greatly stimulated by glutamine and that Mn(2+) is required.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Molecular basis for the distinct divalent cation requirement in the uridylylation of the signal transduction proteins GlnJ and GlnB from Rhodospirillum rubrum.BMC Microbiol. 2012 Jul 8;12:136. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-136. BMC Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22769741 Free PMC article.
-
The activity of adenylyltransferase in Rhodospirillum rubrum is only affected by alpha-ketoglutarate and unmodified PII proteins, but not by glutamine, in vitro.FEBS J. 2007 May;274(10):2449-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.05778.x. Epub 2007 Apr 5. FEBS J. 2007. PMID: 17419734
-
Uridylylation of the PII protein from Herbaspirillum seropedicae.Can J Microbiol. 2001 Apr;47(4):309-14. doi: 10.1139/w01-018. Can J Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11358170
-
Purification of P(II) and P(II)-UMP and in vitro studies of regulation of glutamine synthetase in Rhodospirillum rubrum.J Bacteriol. 1999 Oct;181(20):6524-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.181.20.6524-6529.1999. J Bacteriol. 1999. PMID: 10515945 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamine signalling in bacteria.Front Biosci. 2007 Jan 1;12:358-70. doi: 10.2741/2069. Front Biosci. 2007. PMID: 17127304 Review.
Cited by
-
Specificity and regulation of interaction between the PII and AmtB1 proteins in Rhodospirillum rubrum.J Bacteriol. 2007 Oct;189(19):6861-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.00759-07. Epub 2007 Jul 20. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17644595 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of perturbation of ATP level on the activity and regulation of nitrogenase in Rhodospirillum rubrum.J Bacteriol. 2009 Sep;191(17):5526-37. doi: 10.1128/JB.00585-09. Epub 2009 Jun 19. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19542280 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis for the distinct divalent cation requirement in the uridylylation of the signal transduction proteins GlnJ and GlnB from Rhodospirillum rubrum.BMC Microbiol. 2012 Jul 8;12:136. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-136. BMC Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22769741 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and functional characterization of NifA variants that are independent of GlnB activation in the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum.Microbiology (Reading). 2008 Sep;154(Pt 9):2689-2699. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2008/019406-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2008. PMID: 18757802 Free PMC article.
-
Mutagenesis and functional characterization of the four domains of GlnD, a bifunctional nitrogen sensor protein.J Bacteriol. 2010 Jun;192(11):2711-21. doi: 10.1128/JB.01674-09. Epub 2010 Apr 2. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20363937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Araujo, M. S., V. A. Baura, E. M. Souza, E. M. Benelli, L. U. Rigo, M. B. Steffens, F. O. Pedrosa, and L. S. Chubatsu. 2004. In vitro uridylylation of the Azospirillum brasilense N-signal transducing GlnZ protein. Protein Expr. Purif. 33:19-24. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson, M. R., E. S. Kamberov, R. L. Weiss, and A. J. Ninfa. 1994. Reversible uridylylation of the Escherichia coli PII signal transduction protein regulates its ability to stimulate the dephosphorylation of the transcription factor nitrogen regulator I (NRI or NtrC). J. Biol. Chem. 269:28288-28293. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson, M. R., and A. J. Ninfa. 1999. Characterization of the GlnK protein of Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 32:301-313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

