Identification of novel Escherichia coli ribosome-associated proteins using isobaric tags and multidimensional protein identification techniques
- PMID: 17337586
- PMCID: PMC1855874
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00090-07
Identification of novel Escherichia coli ribosome-associated proteins using isobaric tags and multidimensional protein identification techniques
Abstract
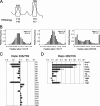
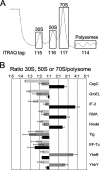
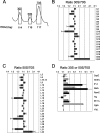
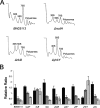
Biogenesis of the large ribosomal subunit requires the coordinate assembly of two rRNAs and 33 ribosomal proteins. In vivo, additional ribosome assembly factors, such as helicases, GTPases, pseudouridine synthetases, and methyltransferases, are also critical for ribosome assembly. To identify novel ribosome-associated proteins, we used a proteomic approach (isotope tagging for relative and absolute quantitation) that allows for semiquantitation of proteins from complex protein mixtures. Ribosomal subunits were separated by sucrose density centrifugation, and the relevant fractions were pooled and analyzed. The utility and reproducibility of the technique were validated via a double duplex labeling method. Next, we examined proteins from 30S, 50S, and translating ribosomes isolated at both 16 degrees C and 37 degrees C. We show that the use of isobaric tags to quantify proteins from these particles is an excellent predictor of the particles with which the proteins associate. Moreover, in addition to bona fide ribosomal proteins, additional proteins that comigrated with different ribosomal particles were detected, including both known ribosomal assembly factors and unknown proteins. The ribosome association of several of these proteins, as well as others predicted to be associated with ribosomes, was verified by immunoblotting. Curiously, deletion mutants for the majority of these ribosome-associated proteins had little effect on cell growth or on the polyribosome profiles.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Escherichia coli GTPase CgtAE is involved in late steps of large ribosome assembly.J Bacteriol. 2006 Oct;188(19):6757-70. doi: 10.1128/JB.00444-06. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16980477 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of the proteins of the bacterial ribosome using QconCAT technology.J Proteome Res. 2014 Mar 7;13(3):1211-22. doi: 10.1021/pr400667h. Epub 2014 Feb 12. J Proteome Res. 2014. PMID: 24494973
-
The tandem GTPase, Der, is essential for the biogenesis of 50S ribosomal subunits in Escherichia coli.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Sep;61(6):1660-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05348.x. Epub 2006 Aug 23. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16930151
-
Structural studies of E. coli ribosomes by spectroscopic techniques: a specialized review.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2005 Dec;62(4-5):1070-80. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2005.04.032. Epub 2005 Jun 9. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2005. PMID: 15950526 Review.
-
A surfeit of factors: why is ribosome assembly so much more complicated in eukaryotes than bacteria?RNA Biol. 2004 May;1(1):10-5. Epub 2004 May 19. RNA Biol. 2004. PMID: 17194932 Review.
Cited by
-
E. coli metabolic protein aldehyde-alcohol dehydrogenase-E binds to the ribosome: a unique moonlighting action revealed.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 29;6:19936. doi: 10.1038/srep19936. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26822933 Free PMC article.
-
YqjD is an inner membrane protein associated with stationary-phase ribosomes in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2012 Aug;194(16):4178-83. doi: 10.1128/JB.00396-12. Epub 2012 Jun 1. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22661687 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative bacterial proteomics: analysis of the core genome concept.PLoS One. 2008 Feb 6;3(2):e1542. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001542. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18253490 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of tetratricopeptide repeat-like proteins in Francisella tularensis and identification of a novel locus required for virulence.Infect Immun. 2014 Dec;82(12):5035-48. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01620-14. Epub 2014 Sep 22. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 25245806 Free PMC article.
-
Persistence as a Constituent of a Biocontrol Mechanism (Competition for Nutrients and Niches) in Pseudomonas putida PCL1760.Microorganisms. 2022 Dec 21;11(1):19. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11010019. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36677311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bessman, M. J., J. D. Walsh, C. A. Dunn, J. Swaminathan, J. E. Weldon, and J. Shen. 2001. The gene ygdP, associated with the invasiveness of Escherichia coli K1, designates a Nudix hydrolase, Orf176, active on adenosine (5′)-pentaphospho-(5′)-adenosine (Ap5A). J. Biol. Chem. 276:37834-37838. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

