Effect of suckling on the peripheral sensitivity of full-term newborn infants
- PMID: 17337659
- PMCID: PMC2675458
- DOI: 10.1136/adc.2006.097931
Effect of suckling on the peripheral sensitivity of full-term newborn infants
Abstract
Background: Sucking may reduce the manifestations of pain in newborn infants.
Objective: To examine the effect of suckling on the threshold for peripheral somatosensory responses.
Subjects and methods: Graded Von Frey filaments were applied to the heel to initiate peripheral somatosensory responses (withdrawal reflex and gross body movements) in term infants.
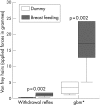
Results: Dummy sucking increases the somatosensory threshold, but breast feeding had a more marked effect, increasing the threshold of the flexion withdrawal reflex (p<or=0.002) and the threshold for gross body movements (p</=0.002).
Conclusion: Peripheral sensitivity of newborn infants is considerably reduced during sucking, particularly at the breast.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
References
-
- Wong C M, McIntosh N, Menon G.et al The pain (and stress) in infants in a neonatal intensive care unit. In: Schechter NL, Berde CB, Yaster M, eds. Pain in infants, children and adolescents. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2003669–692.
-
- Stevens B, Ohlsson A. Sucrose for analgesia in newborn infants undergoing painful procedures. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2000(2)CD001069 - PubMed
-
- Willer J C. Studies on pain. Effects of morphine on a spinal nociceptive flexion reflex and related pain sensation in man. Brain Res 1985331105–114. - PubMed
-
- Blass E M, Fitzgerald E. Milk induced analgesia and comforting in 10 day old rats: opioid mediation. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1988299–13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources