Plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 and left ventricular remodelling after acute myocardial infarction in man: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 17339265
- PMCID: PMC2202923
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehm003
Plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 and left ventricular remodelling after acute myocardial infarction in man: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Aim: To describe temporal profiles of plasma matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9), and their relationship with echocardiographic (Echo) parameters of left ventricular (LV) function and remodelling, after acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in man.
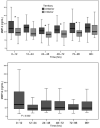
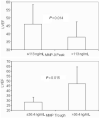
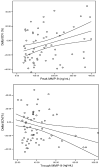
Methods and results: Plasma MMP-2 and MMP-9 were assayed at intervals (0-12, 12-24, 24-48, 48-72, 72-96, and > 96 h) in 91 patients with AMI (ST-elevation/non-ST-elevation 77/24; 73% male; 40% anterior site) and on a single occasion in 172 age- and sex-matched control subjects with stable coronary artery disease. Echo assessment of LV volumes, LV ejection fraction (LVEF), and wall motion index score were assessed before discharge and at follow-up (median 176, range 138-262 days) for patients and on a single occassion in controls. Plasma MMP-2 was similar at all times after AMI, elevated when compared with control (P = 0.005-0.001) and unrelated to LV function or volume during index admission or at follow-up. Maximal MMP-9 was seen at 0-12 h and was elevated when compared with control (P = 0.002) followed by fall to a plateau. Both maximal and plateau MMP-9 concentration correlated with white blood cell (WBC, P = 0.023 to < 0.001) and neutrophil count (P = 0.014 to < 0.001). Maximal MMP-9 had independent predictive value for lower LVEF (P = 0.004) during admission and for greater change in LV end-diastolic volume between admission and follow-up (R = 0.3, P = 0.016). In contrast, higher plateau levels of MMP-9 were associated with relative preservation of LV function (increasing LVEF, P = 0.002; decreasing WMIS, P = 0.009) and less change in end-systolic volume and end-diastolic volumes after discharge (P = 0.001 and 0.024, respectively).
Conclusion: Both MMP-9 and MMP-2 are elevated following AMI. The biphasic profile of plasma MMP-9 is related to LV remodelling and function following AMI in man. Higher early levels of MMP-9 associate with the extent of LV remodelling and circulating WBC levels. In contrast, higher plateau levels later after AMI are associated with relative preservation of LV function. Temporal profile, rather than absolute magnitude, of MMP-9 activity appears to be important for LV remodelling after AMI.
Figures
Comment in
-
Matrix metalloproteinase and heart failure: is it time to move from research to clinical laboratories?Eur Heart J. 2007 Mar;28(6):659-60. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehl574. Epub 2007 Mar 8. Eur Heart J. 2007. PMID: 17347173 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Plasma tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 and matrix metalloproteinase-9: novel indicators of left ventricular remodelling and prognosis after acute myocardial infarction.Eur Heart J. 2008 Sep;29(17):2116-24. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehn315. Epub 2008 Jul 8. Eur Heart J. 2008. PMID: 18614523 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma MMP-2, MMP-9 and N-BNP in long-term survivors following complicated myocardial infarction: relation to cardiac magnetic resonance imaging measures of left ventricular structure and function.J Card Fail. 2007 Dec;13(10):843-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2007.07.006. J Card Fail. 2007. PMID: 18068618 Clinical Trial.
-
Circulating stromelysin-1 (MMP-3): a novel predictor of LV dysfunction, remodelling and all-cause mortality after acute myocardial infarction.Eur J Heart Fail. 2008 Feb;10(2):133-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejheart.2007.12.009. Epub 2008 Jan 30. Eur J Heart Fail. 2008. PMID: 18234553 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced cardiac production of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 and its attenuation associated with pravastatin treatment in patients with acute myocardial infarction.Clin Sci (Lond). 2007 Jan;112(1):43-9. doi: 10.1042/CS20060110. Clin Sci (Lond). 2007. PMID: 16939410
-
Possible mechanism by which renal sympathetic denervation improves left ventricular remodelling after myocardial infarction.Exp Physiol. 2016 Feb;101(2):260-71. doi: 10.1113/EP085302. Epub 2015 Dec 16. Exp Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26556551
Cited by
-
Transgenic overexpression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in macrophages attenuates the inflammatory response and improves left ventricular function post-myocardial infarction.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012 Nov;53(5):599-608. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.07.017. Epub 2012 Aug 3. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22884843 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers in acute myocardial infarction.BMC Med. 2010 Jun 7;8:34. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-8-34. BMC Med. 2010. PMID: 20529285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of polymorphisms of zinc metalloproteinases with clinical response to stem cell therapy.Herz. 2010 Aug;35(5):309-16. doi: 10.1007/s00059-010-3353-z. Herz. 2010. PMID: 20625691 Clinical Trial.
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 functional promoter polymorphism 1562C>T increased risk of early-onset coronary artery disease.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Jan;39(1):555-62. doi: 10.1007/s11033-011-0770-x. Epub 2011 May 11. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 21559835
-
Prevention of late postmyocardial infarction left ventricular remodeling: an update.Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2009 Dec;6(4):245-53. doi: 10.1007/s11897-009-0034-4. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2009. PMID: 19948093 Review.
References
-
- The Multicenter Postinfarction Research Group Risk stratification and survival after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1983;309:331–336. - PubMed
-
- White HD, Norris RM, Brown MA, Brandt PW, Whitlock RM, Wild CJ. Left ventricular end systolic volume as the major determinant of survival after recovery from myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1987;76:44–51. - PubMed
-
- Pfeffer MA, Braunwald E. Ventricular remodelling after myocardial infarction: experimental observations and clinical implications. Circulation. 1990;81:1161–1172. - PubMed
-
- Peterson JT, Li H, Dillon L, Bryant JW. Evolution of matrix metalloproteinase and tissue inhibitor during heart failure progression in the infarcted rat. Cardiovasc Res. 2000;46:307–315. - PubMed
-
- Etoh T, Joffs C, Deschamps AM, Davis J, Dowdy K, Hendrick J, Baicu S, Muckerjee R, Manhaini M, Spinale FG. Myocardial and interstitial matrix metalloproteinase activity after acute myocardial infarction in pigs. Am J Physiol. 2001;281:H987–H994. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

