Functional genomics identifies a Myb domain-containing protein family required for assembly of CENP-A chromatin
- PMID: 17339379
- PMCID: PMC2064049
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200701065
Functional genomics identifies a Myb domain-containing protein family required for assembly of CENP-A chromatin
Abstract
Nucleosomes containing the centromere-specific histone H3 variant centromere protein A (CENP-A) create the chromatin foundation for kinetochore assembly. To understand the mechanisms that selectively target CENP-A to centromeres, we took a functional genomics approach in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, in which failure to load CENP-A results in a signature kinetochore-null (KNL) phenotype. We identified a single protein, KNL-2, that is specifically required for CENP-A incorporation into chromatin. KNL-2 and CENP-A localize to centromeres throughout the cell cycle in an interdependent manner and coordinately direct chromosome condensation, kinetochore assembly, and chromosome segregation. The isolation of KNL-2-associated chromatin coenriched CENP-A, indicating their close proximity on DNA. KNL-2 defines a new conserved family of Myb DNA-binding domain-containing proteins. The human homologue of KNL-2 is also specifically required for CENP-A loading and kinetochore assembly but is only transiently present at centromeres after mitotic exit. These results implicate a new protein class in the assembly of centromeric chromatin and suggest that holocentric and monocentric chromosomes share a common mechanism for CENP-A loading.
Figures
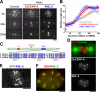
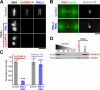
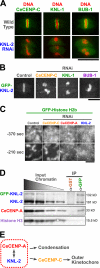

Comment in
-
Centromeric chromatin gets loaded.J Cell Biol. 2007 Mar 12;176(6):735-6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200702020. Epub 2007 Mar 5. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17339381 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aasland, R., A.F. Stewart, and T. Gibson. 1996. The SANT domain: a putative DNA-binding domain in the SWI-SNF and ADA complexes, the transcriptional co-repressor N-CoR and TFIIIB. Trends Biochem. Sci. 21:87–88. - PubMed
-
- Buchwitz, B.J., K. Ahmad, L.L. Moore, M.B. Roth, and S. Henikoff. 1999. A histone-H3-like protein in C. elegans. Nature. 401:547–548. - PubMed
-
- Choo, K.H. 2000. Centromerization. Trends Cell Biol. 10:182–188. - PubMed
-
- Cleveland, D.W., Y. Mao, and K.F. Sullivan. 2003. Centromeres and kinetochores: from epigenetics to mitotic checkpoint signaling. Cell. 112:407–421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

