Friend of GATA-1-independent transcriptional repression: a novel mode of GATA-1 function
- PMID: 17339418
- PMCID: PMC1890840
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-02-072983
Friend of GATA-1-independent transcriptional repression: a novel mode of GATA-1 function
Abstract
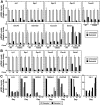
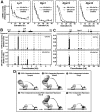
The GATA-1-interacting protein Friend Of GATA-1 (FOG-1) is essential for the proper transcriptional activation and repression of numerous GATA-1 target genes. Although FOG-1-independent activation by GATA-1 has been described, all known examples of GATA-1-mediated repression are FOG-1 dependent. In the GATA-1-null G1E cell line, estrogen receptor ligand binding domain (ER) chimeras of either wild-type GATA-1 or a FOG-1-binding defective mutant of GATA-1 repressed several genes similarly upon activation with beta-estradiol. Repression also occurred in a FOG-1-null cell line expressing ER-GATA-1 and during ex vivo erythropoiesis. At the Lyl1 and Rgs18 loci, we found highly restricted occupancy by GATA-1 and GATA-2, indicating that these genes are direct targets of GATA factor regulation. The identification of genes repressed by GATA-1 independent of FOG-1 defines a novel mode of GATA-1-mediated transcriptional regulation.
Figures
References
-
- Tsang AP, Visvader JE, Turner CA, et al. FOG, a multitype zinc finger protein, acts as a cofactor for transcription factor GATA-1 in erythroid and megakaryocytic differentiation. Cell. 1997;90:109–119. - PubMed
-
- Crispino JD, Lodish MB, MacKay JP, Orkin SH. Use of altered specificity mutants to probe a specific protein-protein interaction in differentiation: the GATA-1:FOG complex. Mol Cell. 1999;3:219–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

