Site-directed transposon integration in human cells
- PMID: 17344320
- PMCID: PMC1874657
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm089
Site-directed transposon integration in human cells
Abstract
The Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposon is a promising gene transfer vector that integrates nonspecifically into host cell genomes. Herein, we attempt to direct transposon integration into predetermined DNA sites by coupling a site-specific DNA-binding domain (DBD) to the SB transposase. We engineered fusion proteins comprised of a hyperactive SB transposase (HSB5) joined via a variable-length linker to either end of the polydactyl zinc-finger protein E2C, which binds a unique sequence on human chromosome 17. Although DBD linkage to the C-terminus of SB abolished activity in a human cell transposition assay, the N-terminal addition of the E2C or Gal4 DBD did not. Molecular analyses indicated that these DBD-SB fusion proteins retained DNA-binding specificity for their respective substrate molecules and were capable of mediating bona fide transposition reactions. We also characterized transposon integrations in the presence of the E2C-SB fusion protein to determine its potential to target predefined DNA sites. Our results indicate that fusion protein-mediated tethering can effectively redirect transposon insertion site selection in human cells, but suggest that stable docking of integration complexes may also partially interfere with the cut-and-paste mechanism. These findings illustrate the feasibility of directed transposon integration and highlight potential means for future development.
Figures
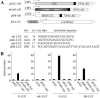


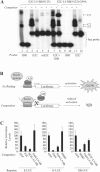
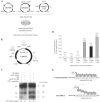
References
-
- Hacein-Bey-Abina S, Le Deist F, Carlier F, Bouneaud C, Hue C, De Villartay JP, Thrasher AJ, Wulffraat N, Sorensen R, et al. Sustained correction of X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency by ex vivo gene therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002;346:1185–1193. - PubMed
-
- Hacein-Bey-Abina S, von Kalle C, Schmidt M, Le Deist F, Wulffraat N, McIntyre E, Radford I, Villeval JL, Fraser CC, et al. A serious adverse event after successful gene therapy for X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:255–256. - PubMed
-
- Hacein-Bey-Abina S, Von Kalle C, Schmidt M, McCormack MP, Wulffraat N, Leboulch P, Lim A, Osborne CS, Pawliuk R, et al. LMO2-associated clonal T cell proliferation in two patients after gene therapy for SCID-X1. Science. 2003;302:415–419. - PubMed
-
- Thomas CE, Ehrhardt A, Kay MA. Progress and problems with the use of viral vectors for gene therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2003;4:346–358. - PubMed
-
- Katz RA, Merkel G, Skalka AM. Targeting of retroviral integrase by fusion to a heterologous DNA binding domain: in vitro activities and incorporation of a fusion protein into viral particles. Virology. 1996;217:178–190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

