Selective ablation of proliferating microglial cells exacerbates ischemic injury in the brain
- PMID: 17344397
- PMCID: PMC6672496
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5360-06.2007
Selective ablation of proliferating microglial cells exacerbates ischemic injury in the brain
Abstract
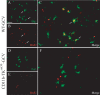
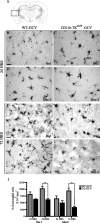
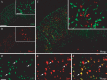
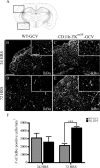
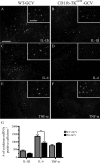
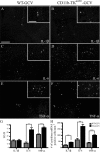
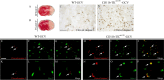
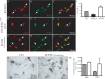
Here we report in vivo evidence of a neuroprotective role of proliferating microglial cells in cerebral ischemia. Using transgenic mice expressing a mutant thymidine kinase form of herpes simplex virus driven by myeloid-specific CD11b promoter and ganciclovir treatment as a tool, we selectively ablated proliferating (Mac-2 positive) microglia after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. The series of experiments using green fluorescent protein-chimeric mice demonstrated that within the first 72 h after ischemic injury, the Mac-2 marker [unlike Iba1 (ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1)] was preferentially expressed by the resident microglia. Selective ablation of proliferating resident microglia was associated with a marked alteration in the temporal dynamics of proinflammatory cytokine expression, a significant increase in the size of infarction associated with a 2.7-fold increase in the number of apoptotic cells, predominantly neurons, and a 1.8-fold decrease in the levels of IGF-1. A double-immunofluorescence analysis revealed a approximately 100% colocalization between IGF-1 positive cells and Mac-2, a marker of activated/proliferating resident microglia. Conversely, stimulation of microglial proliferation after cerebral ischemia by M-CSF (macrophage colony stimulating factor) resulted in a 1.9-fold increase in IGF-1 levels and a significant increase of Mac2+ cells. Our findings suggest that a postischemic proliferation of the resident microglial cells may serve as an important modulator of a brain inflammatory response. More importantly, our results revealed a marked neuroprotective potential of proliferating microglia serving as an endogenous pool of neurotrophic molecules such as IGF-1, which may open new therapeutic avenues in the treatment of stroke and other neurological disorders.
Figures
References
-
- Allan SM, Rothwell NJ. Cytokines and acute neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:734–744. - PubMed
-
- Batchelor PE, Liberatore GT, Wong JY, Porritt MJ, Frerichs F, Donnan GA, Howells DW. Activated macrophages and microglia induce dopaminergic sprouting in the injured striatum and express brain-derived neurotrophic factor and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. J Neurosci. 1999;19:1708–1716. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu JM, Kriz J, Julien JP. Induction of peripherin expression in subsets of brain neurons after lesion injury or cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2002;946:153–161. - PubMed
-
- Beilharz EJ, Russo VC, Butler G, Baker NL, Connor B, Sirimanne ES, Dragunow M, Werther GA, Gluckman PD, Williams CE, Scheepens A. Co-ordinated and cellular specific induction of the components of the IGF/IGFBP axis in the rat brain following hypoxic-ischemic injury. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1998;59:119–134. - PubMed
-
- Belayev L, Busto R, Zhao W, Fernandez G, Ginsberg MD. Middle cerebral artery occlusion in the mouse by intraluminal suture coated with poly-L-lysine: neurological and histological validation. Brain Res. 1999;833:181–190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
