The Polycomb group proteins bind throughout the INK4A-ARF locus and are disassociated in senescent cells
- PMID: 17344414
- PMCID: PMC1820894
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.415507
The Polycomb group proteins bind throughout the INK4A-ARF locus and are disassociated in senescent cells
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: The Polycomb group proteins bind throughout the INK4A-ARF locus and are disassociated in senescent cells.Genes Dev. 2023 Sep 1;37(17-18):861. doi: 10.1101/gad.351178.123. Genes Dev. 2023. PMID: 37852794 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
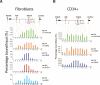
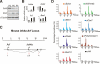
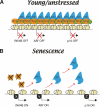
The p16INK4A and p14ARF proteins, encoded by the INK4A-ARF locus, are key regulators of cellular senescence, yet the mechanisms triggering their up-regulation are not well understood. Here, we show that the ability of the oncogene BMI1 to repress the INK4A-ARF locus requires its direct association and is dependent on the continued presence of the EZH2-containing Polycomb-Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) complex. Significantly, EZH2 is down-regulated in stressed and senescing populations of cells, coinciding with decreased levels of associated H3K27me3, displacement of BMI1, and activation of transcription. These results provide a model for how the INK4A-ARF locus is activated and how Polycombs contribute to cancer.
Figures


References
-
- Alcorta D.A., Xiong Y., Phelps D., Hannon G., Beach D., Barrett J.C., Xiong Y., Phelps D., Hannon G., Beach D., Barrett J.C., Phelps D., Hannon G., Beach D., Barrett J.C., Hannon G., Beach D., Barrett J.C., Beach D., Barrett J.C., Barrett J.C. Involvement of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16 (INK4a) in replicative senescence of normal human fibroblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1996;93:13742–13747. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boyer L.A., Plath K., Zeitlinger J., Brambrink T., Medeiros L.A., Lee T.I., Levine S.S., Wernig M., Tajonar A., Ray M.K., Plath K., Zeitlinger J., Brambrink T., Medeiros L.A., Lee T.I., Levine S.S., Wernig M., Tajonar A., Ray M.K., Zeitlinger J., Brambrink T., Medeiros L.A., Lee T.I., Levine S.S., Wernig M., Tajonar A., Ray M.K., Brambrink T., Medeiros L.A., Lee T.I., Levine S.S., Wernig M., Tajonar A., Ray M.K., Medeiros L.A., Lee T.I., Levine S.S., Wernig M., Tajonar A., Ray M.K., Lee T.I., Levine S.S., Wernig M., Tajonar A., Ray M.K., Levine S.S., Wernig M., Tajonar A., Ray M.K., Wernig M., Tajonar A., Ray M.K., Tajonar A., Ray M.K., Ray M.K., et al. Polycomb complexes repress developmental regulators in murine embryonic stem cells. Nature. 2006;441:349–353. - PubMed
-
- Bracken A.P., Pasini D., Capra M., Prosperini E., Colli E., Helin K., Pasini D., Capra M., Prosperini E., Colli E., Helin K., Capra M., Prosperini E., Colli E., Helin K., Prosperini E., Colli E., Helin K., Colli E., Helin K., Helin K. EZH2 is downstream of the pRB–E2F pathway, essential for proliferation and amplified in cancer. EMBO J. 2003;22:5323–5335. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bracken A.P., Dietrich N., Pasini D., Hansen K.H., Helin K., Dietrich N., Pasini D., Hansen K.H., Helin K., Pasini D., Hansen K.H., Helin K., Hansen K.H., Helin K., Helin K. Genome-wide mapping of Polycomb target genes unravels their roles in cell fate transitions. Genes & Dev. 2006;20:1123–1136. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bruggeman S.W., Valk-Lingbeek M.E., van der Stoop P.P., Jacobs J.J., Kieboom K., Tanger E., Hulsman D., Leung C., Arsenijevic Y., Marino S., Valk-Lingbeek M.E., van der Stoop P.P., Jacobs J.J., Kieboom K., Tanger E., Hulsman D., Leung C., Arsenijevic Y., Marino S., van der Stoop P.P., Jacobs J.J., Kieboom K., Tanger E., Hulsman D., Leung C., Arsenijevic Y., Marino S., Jacobs J.J., Kieboom K., Tanger E., Hulsman D., Leung C., Arsenijevic Y., Marino S., Kieboom K., Tanger E., Hulsman D., Leung C., Arsenijevic Y., Marino S., Tanger E., Hulsman D., Leung C., Arsenijevic Y., Marino S., Hulsman D., Leung C., Arsenijevic Y., Marino S., Leung C., Arsenijevic Y., Marino S., Arsenijevic Y., Marino S., Marino S., et al. Ink4a and Arf differentially affect cell proliferation and neural stem cell self-renewal in Bmi1-deficient mice. Genes & Dev. 2005;19:1438–1443. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
