Dynamic regulation of miRNA expression in ordered stages of cellular development
- PMID: 17344418
- PMCID: PMC1820899
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1522907
Dynamic regulation of miRNA expression in ordered stages of cellular development
Abstract
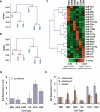
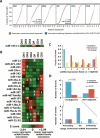
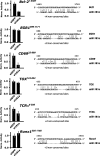
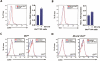
Short RNA expression in several distinct stages of T-lymphocyte development was comprehensively profiled. The total number of microRNAs (miRNAs) expressed per cell at different stages of development varies over nearly an order of magnitude in parallel with changes in total cellular RNA content, suggesting that global miRNA levels are coregulated with the translational capacity of the cell. However, individual miRNAs were dynamically regulated during T-cell development, with at least one miRNA or miRNA family overrepresented at each developmental stage. miRNA regulation in this developmental pathway is characterized by analog rather than switch-like behavior, with temporal enrichments at distinct stages of development observed against a background of constant, basal expression of the miRNA. Enrichments of these miRNAs are temporally correlated with depletions of the transcript levels of targets containing seed matches to the specific miRNAs, and may have specific functional consequences. miR-181a, which is specifically enriched at the CD4(+)CD8(+) (DP) stage of thymocyte development, can repress the expression of Bcl-2, CD69, and the T-cell receptor, all of which are coordinately involved in positive selection.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A miRNA signature of prion induced neurodegeneration.PLoS One. 2008;3(11):e3652. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003652. Epub 2008 Nov 6. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18987751 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary analysis of miRNA pathway in Schistosoma mansoni.Parasitol Int. 2009 Mar;58(1):61-8. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2008.10.002. Epub 2008 Oct 28. Parasitol Int. 2009. PMID: 19007911
-
Prediction and verification of miRNA expression in human and rat retinas.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007 Sep;48(9):3962-7. doi: 10.1167/iovs.06-1221. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007. PMID: 17724173
-
MicroRNAs and immunity: novel players in the regulation of normal immune function and inflammation.Semin Cancer Biol. 2008 Apr;18(2):131-40. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2008.01.005. Epub 2008 Jan 15. Semin Cancer Biol. 2008. PMID: 18291670 Review.
-
MicroRNAs: all gone and then what?Curr Biol. 2005 May 24;15(10):R387-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.05.006. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 15916942 Review.
Cited by
-
CyCoNP lncRNA establishes cis and trans RNA-RNA interactions to supervise neuron physiology.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Sep 9;52(16):9936-9952. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae590. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38989616 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in the regulation of Th17/Treg homeostasis and their potential role in uveitis.Front Genet. 2022 Sep 14;13:848985. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.848985. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36186459 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA profiling of naïve, effector and memory CD8 T cells.PLoS One. 2007 Oct 10;2(10):e1020. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001020. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17925868 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA miR-21 Is Largely Dispensable for Intrathymic T-Cell Development.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 5;9:2497. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02497. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30455689 Free PMC article.
-
The Multifaceted Interface Between Cytokines and microRNAs: An Ancient Mechanism to Regulate the Good and the Bad of Inflammation.Front Immunol. 2018 Dec 21;9:3012. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03012. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30622533 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alfonso C., McHeyzer-Williams M.G., Rosen H., McHeyzer-Williams M.G., Rosen H., Rosen H. CD69 down-modulation and inhibition of thymic egress by short- and long-term selective chemical agonism of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006;36:149–159. - PubMed
-
- Aravin A., Tuschl T., Tuschl T. Identification and characterization of small RNAs involved in RNA silencing. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:5830–5840. - PubMed
-
- Bagga S., Bracht J., Hunter S., Massirer K., Holtz J., Eachus R., Pasquinelli A.E., Bracht J., Hunter S., Massirer K., Holtz J., Eachus R., Pasquinelli A.E., Hunter S., Massirer K., Holtz J., Eachus R., Pasquinelli A.E., Massirer K., Holtz J., Eachus R., Pasquinelli A.E., Holtz J., Eachus R., Pasquinelli A.E., Eachus R., Pasquinelli A.E., Pasquinelli A.E. Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell. 2005;122:553–563. - PubMed
-
- Bonifacino J.S., McCarthy S.A., Maguire J.E., Nakayama T., Singer D.S., Klausner R.D., Singer A., McCarthy S.A., Maguire J.E., Nakayama T., Singer D.S., Klausner R.D., Singer A., Maguire J.E., Nakayama T., Singer D.S., Klausner R.D., Singer A., Nakayama T., Singer D.S., Klausner R.D., Singer A., Singer D.S., Klausner R.D., Singer A., Klausner R.D., Singer A., Singer A. Novel post-translational regulation of TCR expression in CD4+CD8+ thymocytes influenced by CD4. Nature. 1990;344:247–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
