Maternal intake of vitamin D during pregnancy and risk of recurrent wheeze in children at 3 y of age
- PMID: 17344501
- PMCID: PMC4406411
- DOI: 10.1093/ajcn/85.3.788
Maternal intake of vitamin D during pregnancy and risk of recurrent wheeze in children at 3 y of age
Abstract
Background: Vitamin D deficiency and asthma are common at higher latitudes. Although vitamin D has important immunologic effects, its relation with asthma is unknown.
Objective: We hypothesized that a higher maternal intake of vitamin D during pregnancy is associated with a lower risk of recurrent wheeze in children at 3 y of age.
Design: The participants were 1194 mother-child pairs in Project Viva-a prospective prebirth cohort study in Massachusetts. We assessed the maternal intake of vitamin D during pregnancy from a validated food-frequency questionnaire. The primary outcome was recurrent wheeze, ie, a positive asthma predictive index (>or=2 wheezing attacks among children with a personal diagnosis of eczema or a parental history of asthma).
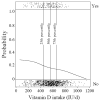
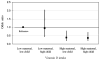
Results: The mean (+/-SD) total vitamin D intake during pregnancy was 548 +/- 167 IU/d. By age 3 y, 186 children (16%) had recurrent wheeze. Compared with mothers in the lowest quartile of daily intake (median: 356 IU), those in the highest quartile (724 IU) had a lower risk of having a child with recurrent wheeze [odds ratio (OR): 0.39; 95% CI: 0.25, 0.62; P for trend < 0.001]. A 100-IU increase in vitamin D intake was associated with lower risk (OR: 0.81; 95% CI: 0.74, 0.89), regardless of whether vitamin D was from the diet (OR: 0.81; 95% CI: 0.69, 0.96) or supplements (OR: 0.82; 95% CI: 0.73, 0.92). Adjustment for 12 potential confounders, including maternal intake of other dietary factors, did not change the results.
Conclusion: In the northeastern United States, a higher maternal intake of vitamin D during pregnancy may decrease the risk of recurrent wheeze in early childhood.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors had a conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Feldman D, Pike JW, Glorieux FH. Vitamin D. 2. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier Academic Press; 2005.
-
- Holick MF. Vitamin D. Importance in the prevention of cancers, type 1 diabetes, heart disease, and osteoporosis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;79:362–71. - PubMed
-
- Webb AR, Kline L, Holick MF. Influence of season and latitude on the cutaneous synthesis of vitamin D3: exposure to winter sunlight in Boston and Edmonton will not promote vitamin D3 synthesis in human skin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988;67:373–8. - PubMed
-
- Thomas MK, Lloyd-Jones DM, Thadhani RI, et al. Hypovitaminosis D in medical inpatients. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:777–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

