Critical enzymes involved in endocannabinoid metabolism
- PMID: 17346227
- PMCID: PMC1939815
- DOI: 10.2174/092986607780090829
Critical enzymes involved in endocannabinoid metabolism
Abstract
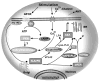
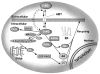
Investigations of the pathways involved in the metabolism of endocannabinoids have grown exponentially in recent years following the discovery of cannabinoid receptors (CB) and their endogenous ligands, such as anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). The in vivo biosynthesis of AEA has been shown to occur through several pathways mediated by N-acylphosphatidylethanolamide-phospholipase D (NAPE-PLD), a secretory PLA(2) and PLC. 2-AG, a second endocannabinoid is generated through the action of selective enzymes such as phosphatidic acid phsophohydrolase, diacylglycerol lipase (DAGL), phosphoinositide-specific PLC (PI-PLC) and lyso-PLC. A putative membrane transporter or facilitated diffusion is involved in the cellular uptake or release of endocannabinoids. AEA is metabolized by fatty acid amidohydrolase (FAAH) and 2-AG is metabolized by both FAAH and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL). The author presents an integrative overview of current research on the enzymes involved in the metabolism of endocannabinoids and discusses possible therapeutic interventions for various diseases, including addiction.
Figures


References
-
- Adams IB, Compton DR, Martin BR. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998;284:1209. - PubMed
-
- Basavarajappa BS. J Clin Res. 2005;11:16.
-
- Basavarajappa BS. In: New Research on Alcoholism. Baye DR, editor. Nova Science Publishers, Inc; New York: 2006. in press.
-
- Basavarajappa BS, Hungund BL. J Neurochem. 1999;72:522. - PubMed
-
- Basavarajappa BS, Saito M, Cooper TB, Hungund BL. Biochemica Biophysica Acta. 2000;1535:78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

