Metabolic control of muscle mitochondrial function and fatty acid oxidation through SIRT1/PGC-1alpha
- PMID: 17347648
- PMCID: PMC1847661
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601633
Metabolic control of muscle mitochondrial function and fatty acid oxidation through SIRT1/PGC-1alpha
Abstract
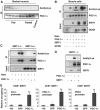
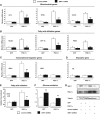
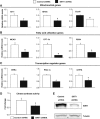
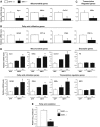
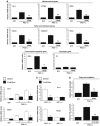
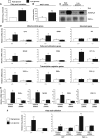
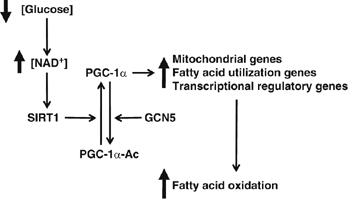
In mammals, maintenance of energy and nutrient homeostasis during food deprivation is accomplished through an increase in mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation in peripheral tissues. An important component that drives this cellular oxidative process is the transcriptional coactivator PGC-1alpha. Here, we show that fasting induced PGC-1alpha deacetylation in skeletal muscle and that SIRT1 deacetylation of PGC-1alpha is required for activation of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation genes. Moreover, expression of the acetyltransferase, GCN5, or the SIRT1 inhibitor, nicotinamide, induces PGC-1alpha acetylation and decreases expression of PGC-1alpha target genes in myotubes. Consistent with a switch from glucose to fatty acid oxidation that occurs in nutrient deprivation states, SIRT1 is required for induction and maintenance of fatty acid oxidation in response to low glucose concentrations. Thus, we have identified SIRT1 as a functional regulator of PGC-1alpha that induces a metabolic gene transcription program of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. These results have implications for understanding selective nutrient adaptation and how it might impact lifespan or metabolic diseases such as obesity and diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Bordone L, Guarente L (2005) Calorie restriction, SIRT1 and metabolism: understanding longevity. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6: 298–305 - PubMed
-
- Chua KF, Mostoslavsky R, Lombard DB, Pang WW, Saito S, Franco S, Kaushal D, Cheng HL, Fischer MR, Stokes N, Murphy MM, Appella E, Alt FW (2005) Mammalian SIRT1 limits replicative lifespan in response to chronic genotoxic stress. Cell Metab 2: 67–76 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

