Reactive oxygen species are essential for autophagy and specifically regulate the activity of Atg4
- PMID: 17347651
- PMCID: PMC1847657
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601623
Reactive oxygen species are essential for autophagy and specifically regulate the activity of Atg4
Erratum in
-
Reactive oxygen species are essential for autophagy and specifically regulate the activity of Atg4.EMBO J. 2019 May 15;38(10):e101812. doi: 10.15252/embj.2019101812. EMBO J. 2019. PMID: 31092559 Free PMC article.
Abstract
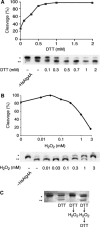
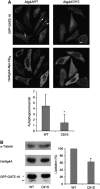
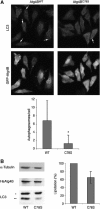
Autophagy is a major catabolic pathway by which eukaryotic cells degrade and recycle macromolecules and organelles. This pathway is activated under environmental stress conditions, during development and in various pathological situations. In this study, we describe the role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) as signaling molecules in starvation-induced autophagy. We show that starvation stimulates formation of ROS, specifically H(2)O(2). These oxidative conditions are essential for autophagy, as treatment with antioxidative agents abolished the formation of autophagosomes and the consequent degradation of proteins. Furthermore, we identify the cysteine protease HsAtg4 as a direct target for oxidation by H(2)O(2), and specify a cysteine residue located near the HsAtg4 catalytic site as a critical for this regulation. Expression of this regulatory mutant prevented the formation of autophagosomes in cells, thus providing a molecular mechanism for redox regulation of the autophagic process.
Figures
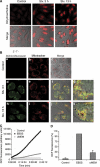
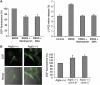
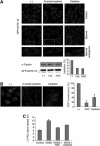
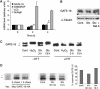

Comment in
-
Oxidation as a post-translational modification that regulates autophagy.Autophagy. 2007 Jul-Aug;3(4):371-3. doi: 10.4161/auto.4214. Epub 2007 Jul 2. Autophagy. 2007. PMID: 17438362
References
-
- Cathcart R, Schwiers E, Ames BN (1983) Detection of picomole levels of hydroperoxides using a fluorescent dichlorofluorescein assay. Anal Biochem 134: 111–116 - PubMed
-
- Chandler JM, Cohen GM, MacFarlane M (1998) Different subcellular distribution of caspase-3 and caspase-7 following Fas-induced apoptosis in mouse liver. J Biol Chem 273: 10815–10818 - PubMed
-
- Codogno P, Meijer AJ (2005) Autophagy and signaling: their role in cell survival and cell death. Cell Death Differ 12 (Suppl 2): 1509–1518 - PubMed
-
- Cuervo AM (2003) Autophagy and aging—when ‘all you can eat' is yourself. Sci Aging Knowledge Environ 2003: pe25. - PubMed
-
- Cuervo AM (2004) Autophagy: in sickness and in health. Trends Cell Biol 14: 70–77 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

