Effects of sleep deprivation on neural functioning: an integrative review
- PMID: 17347797
- PMCID: PMC2778638
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-007-6457-8
Effects of sleep deprivation on neural functioning: an integrative review
Abstract
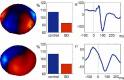
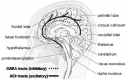
Sleep deprivation has a broad variety of effects on human performance and neural functioning that manifest themselves at different levels of description. On a macroscopic level, sleep deprivation mainly affects executive functions, especially in novel tasks. Macroscopic and mesoscopic effects of sleep deprivation on brain activity include reduced cortical responsiveness to incoming stimuli, reflecting reduced attention. On a microscopic level, sleep deprivation is associated with increased levels of adenosine, a neuromodulator that has a general inhibitory effect on neural activity. The inhibition of cholinergic nuclei appears particularly relevant, as the associated decrease in cortical acetylcholine seems to cause effects of sleep deprivation on macroscopic brain activity. In general, however, the relationships between the neural effects of sleep deprivation across observation scales are poorly understood and uncovering these relationships should be a primary target in future research.
Figures

References
-
- Spiegel K., Leproult R., Van Cauter E. Impact of sleep debt on metabolic and endocrine function. Lancet. 1999;354:1435–1439. - PubMed
-
- van Dongen H.P.A., Rogers N.L., Dinges D.F. Sleep debt: theoretical and empirical issues. Sleep Biol. Rhythms. 2003;1:5–13.
-
- Leonard C., Fanning N., Attwood J., Buckley M. The effect of fatigue, sleep deprivation and onerous working hours on the physical and mental wellbeing of pre-registration house officers. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 1998;167:22–25. - PubMed
-
- Jones K., Harrison Y. Frontal lobe function, sleep loss and fragmented sleep. Sleep Med. Rev. 2001;5:463–475. - PubMed
-
- Bonnet M.H., Arand D.L. Clinical effects of sleep fragmentation versus sleep deprivation. Sleep Med. Rev. 2003;7:297–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

